Converting cryptocurrencies into fiat currencies, such as the euro, is now a much simpler and more straightforward process than in crypto's early days. With the new Trump administration's regulations bringing greater clarity for companies operating in the U.S., and the implementation of MiCA guidelines in Europe, institutions related to crypto are gaining easier access to financial institutions and banks and this regulatory progress is making it increasingly easier and affordable for crypto holders to convert their holdings into euros and transfer them to their bank accounts via bank wire.
The fees for selling crypto to a bank account using the wire section are just 1% and all you have to do is deposit your crypto in the wallet and navigate to the wires section, fill in your bank account details and the amount you wish to receive, submit the request and your bank transfer is on the way. Keep in mind that before you perform the transfer, you need to go through a KYC (know your customer) procedure as this procedure ensures that regulated crypto exchanges like Plasbit work accordingly to the Polish Ministry of Finance, the regulator guidelines, totally unlike the wild west of the early days.
We will explain and show the process of how to transfer crypto from your wallet to your bank account and discuss how this type of transaction compares to other common methods of selling Bitcoin, such as ATMs, debit cards, and P2P.
4 popular methods of selling Bitcoin compared
Let's discuss all options and explain the benefits and drawbacks but you can skip this part if you want to sell your crypto to a bank and get it to your bank account, and head right to the step-by-step walkthrough through the process using PlasBit system and also check what are the fees for selling crypto to a bank account.
Option #1: Wallet to bank account transfer (wire transfer)
Wire transfers are widespread even outside the crypto world, which makes them a well-known and super convenient option. The added safety of using platforms such as Plasbit with double confirmations and KYC procedures ensures it is very difficult to get scammed and lose your money (we will talk about scams and scandals a bit later). All transactions are secured and traceable, putting an extra layer of safety on top of everything.
The downside of this type of transfer (at least for some individuals) is that you need to go through the KYC procedure, which means the transaction is not anonymous. Also, it does take a few days for the transaction to process.
But, overall, PlasBit wire transfers are an excellent option as they combine convenience and security, with a 1% fee for selling crypto to your bank account.
Option #2: Debit and credit cards
Some crypto platforms offer to transfer funds to a credit or debit card tied directly to your accounts. With those, you can convert crypto to fiat using their platform, and the money will be (near) instantly available on your credit card. Convenience and speed are the most significant benefits of credit card transfers.
To those wondering what are the fees for selling crypto to a bank account, the primary issue is high fees, as you will pay the exchange fee and usually pay extra when using the card if it's tied to your account. The second issue is limitations, as both the crypto platform and the bank likely have transfer limits, especially for new accounts. And you can't count on anonymity.
However, platforms like PlasBit issue plastic or virtual cards that are tied directly to the crypto account. With these, you don't need to pay double the fees for the crypto platform and the bank. Instead, you can directly use the card for your everyday payments.
Option #3: Crypto ATMs
If you have a crypto ATM nearby, you can sell Bitcoin privately. You don't need a bank account to do this. Plus, cash will be available instantaneously.
Obviously, the biggest drawback of this method is its availability—cryptocurrency ATMs aren't that common. The second drawback to those wondering what are the fees for selling crypto to a bank account, is super high transaction fees, which can go as high as 20%, with strict transaction limits.
Option #4: P2P transfers
Peer-to-peer transactions happen directly between individual users, and not on centralized exchanges. Because of this, fees are much lower, smaller transactions can go privately, and you can agree on the payment methods and terms.
But, because of all the benefits, scam risks skyrocket. That's why it is super important to use escrow services to protect yourself to an extent. Another issue is that you need to know the market if you don't want to get scammed and that due diligence takes time.
How to transfer funds from your wallet to a bank account using PlasBit
The KYC identity verification procedure, mandatory for all bank transfers, makes the PlasBit wallet super safe. Once you complete it, you will be able to easily transfer crypto to your bank account in a few simple steps:
If you don't already have crypto in your wallet, you will need to deposit it first:
Step 1. After you log in to your PlasBit account, click on the [Wallet] tab.
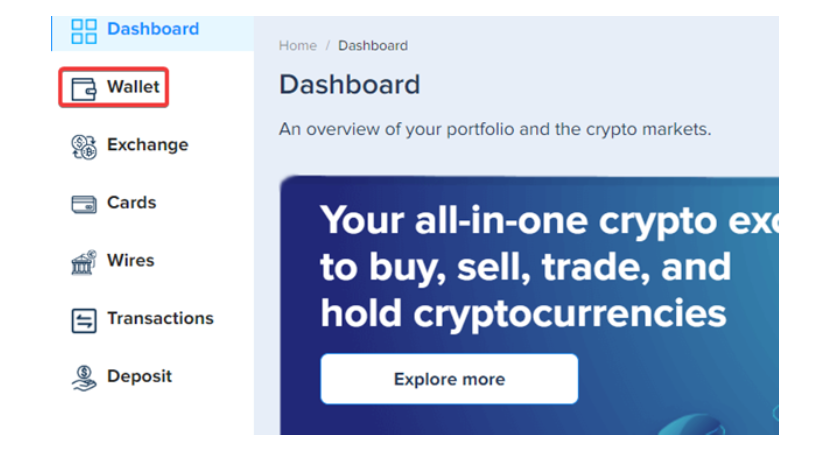
Step 2. There, you can select the type of coin, after which you should click the [Deposit] button and submit the required information.
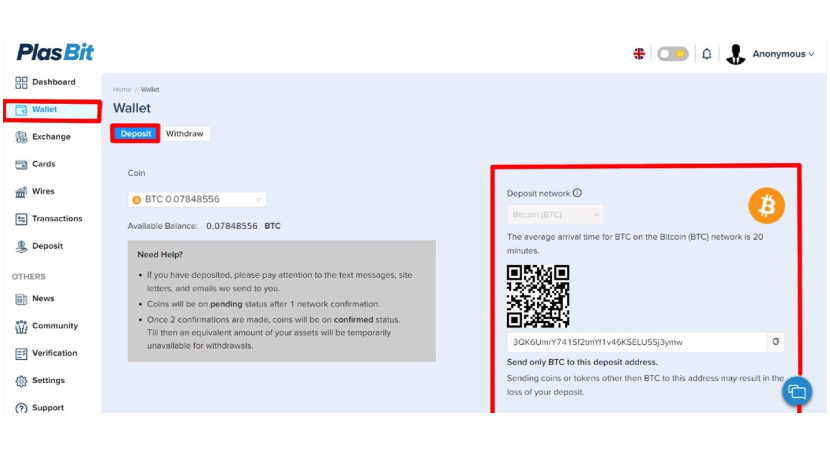
Step 3. Once the Bitcoin is deposited to your Plasbit wallet, Click on the [Wires] tab.
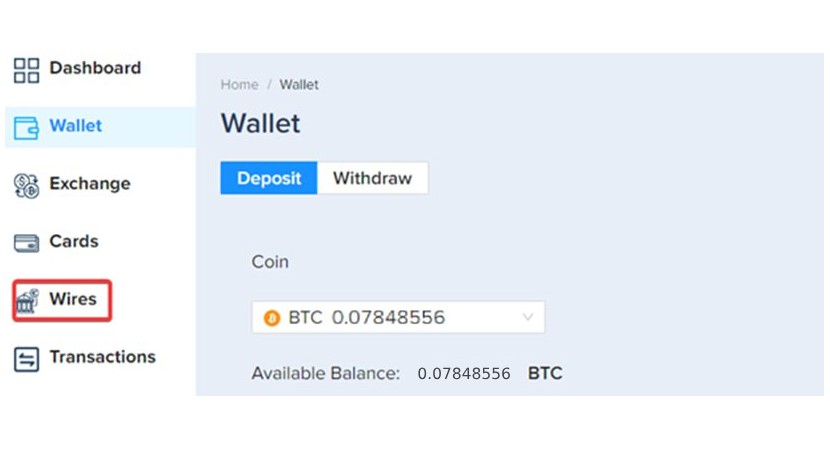
Step 4. After that, you will need to fill out the receiving account details. Note that the name of the receiving bank account holder must match the name of the Plasbit account.
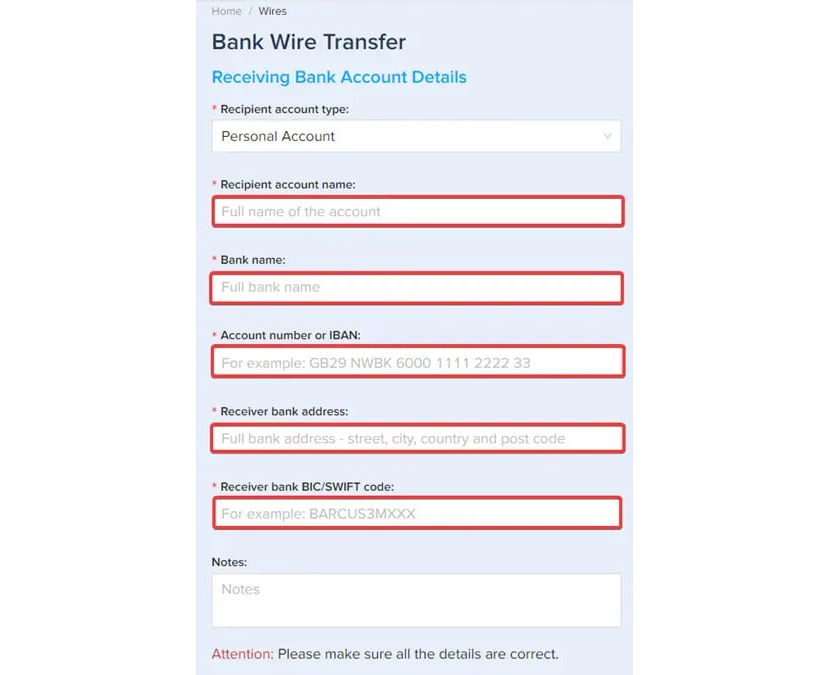
Step 5. The next step is to choose the wallet (we will use Bitcoin for this example).
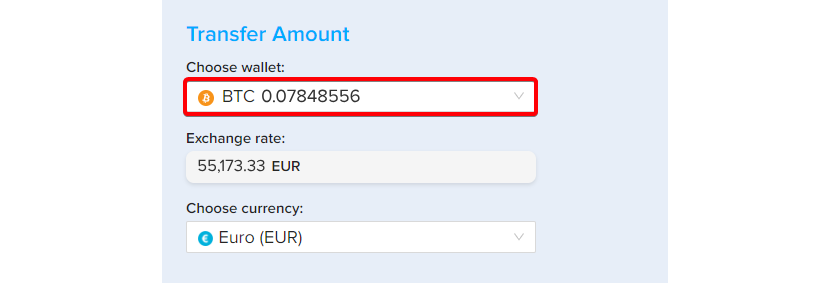
Step 6. The same window lets you select the currency (we will use EUR, which is also applicable if you want to buy crypto with SEPA transfer), and will also display the exchange rate.
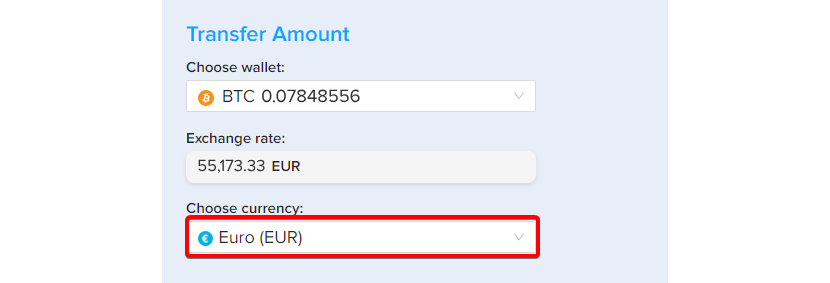
Step 7. To make things super transparent, PlasBit gives you two transfer options.
- If you use the "Amount to transfer" option, you can enter the amount you want to be transferred, on top of which the PlasBit fee will be applied. This option is useful to ensure you have an exact amount of money in your bank account after the exchange without worrying about how much will be transferred after the fees are applied.
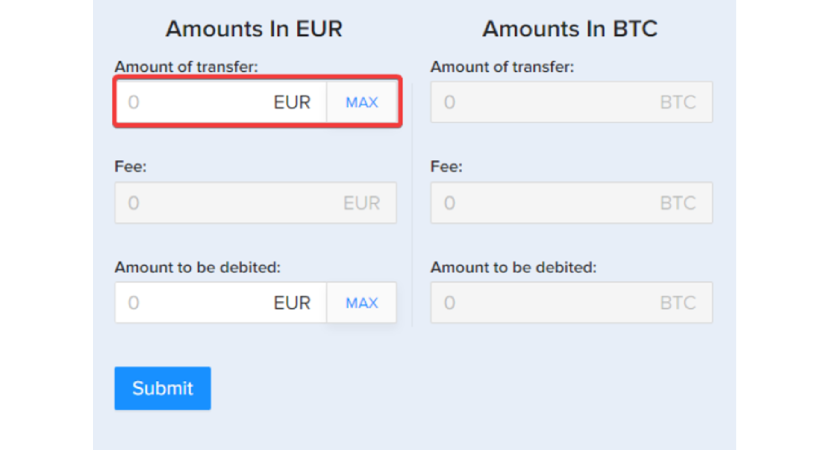
- If you use the "Amount to be debited" field, you can enter the total amount deducted from the wallet, including fees. This is useful to avoid worrying about what are the fees for selling crypto to a bank account, as they are included in the total amount you enter.
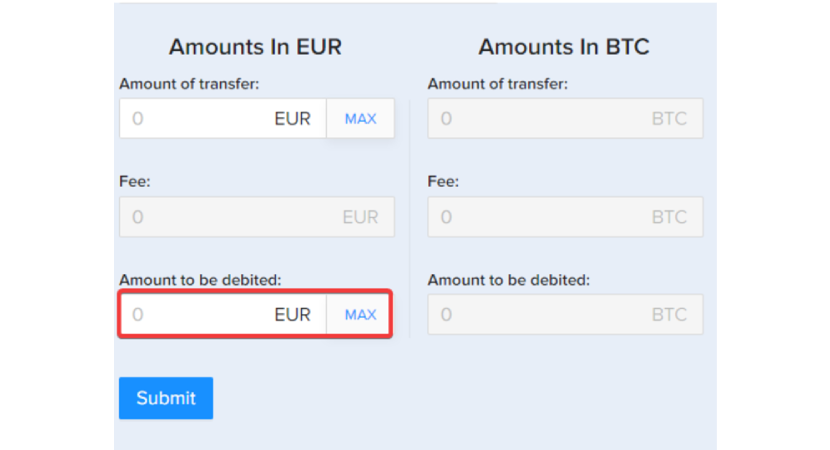
After you have filled in the information, the last step is to click [Submit].
Important note: If you haven't completed the KYC verification process yet, you can do it by clicking on the link at the bottom of your screen. You must go through KYC before completing the crypto to bank account transfer.
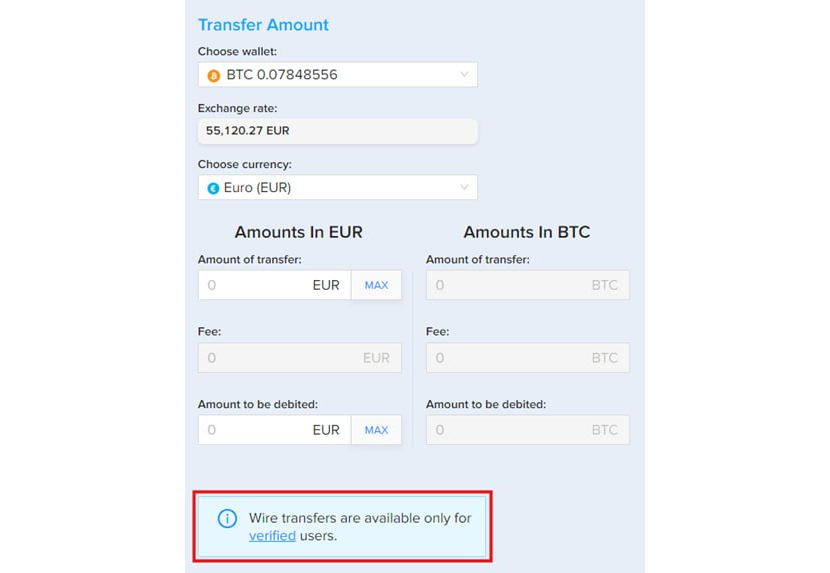
Step 8. The next step is to check the details one more time, and to [Submit] the request if everything is correct.
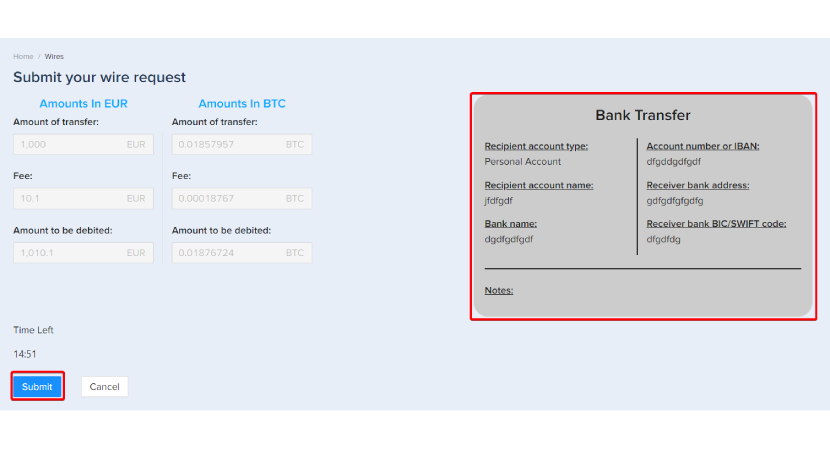
Step 9. After that, you'll need to confirm your identity via two-step authentication by using both your email address and mobile phone number. Click [Send] to receive the codes.
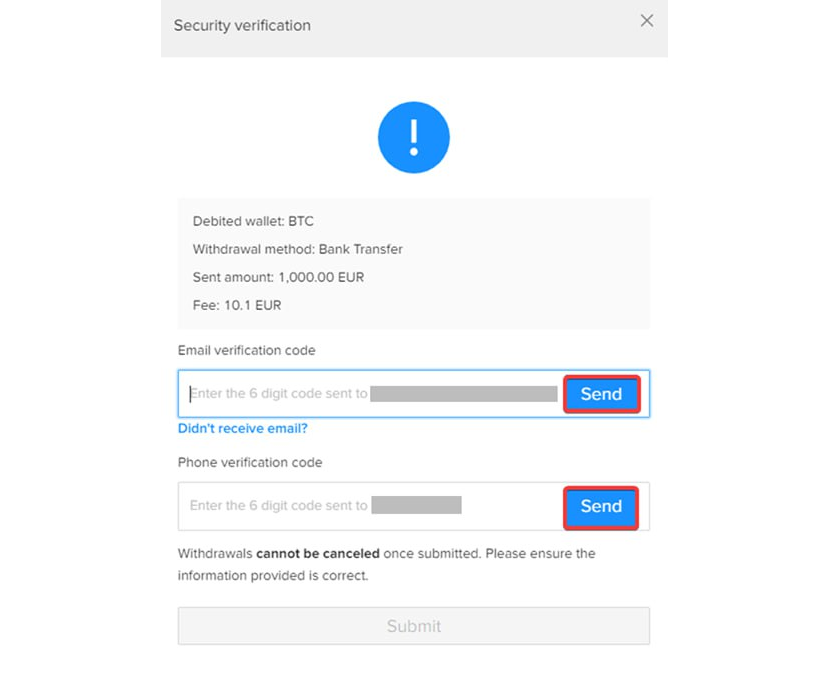
Step 10. Next, you need to enter both the email and SMS codes you received and click [Submit].
Step 11. After you complete, you will receive a "Wire Request Submitted" email to confirm you have gone through the procedure correctly.
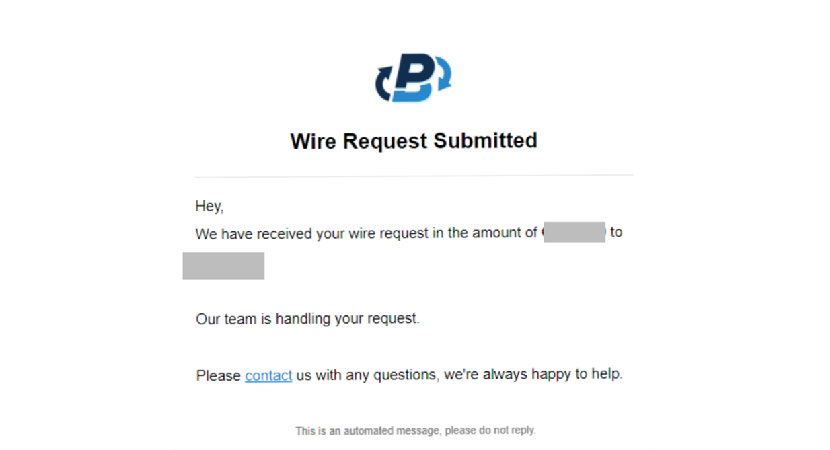
After we approve the request, you will receive a "Wire Request Approved" email as a confirmation.

The money will show on your bank account in 0-5 days after processing the wire transfer.
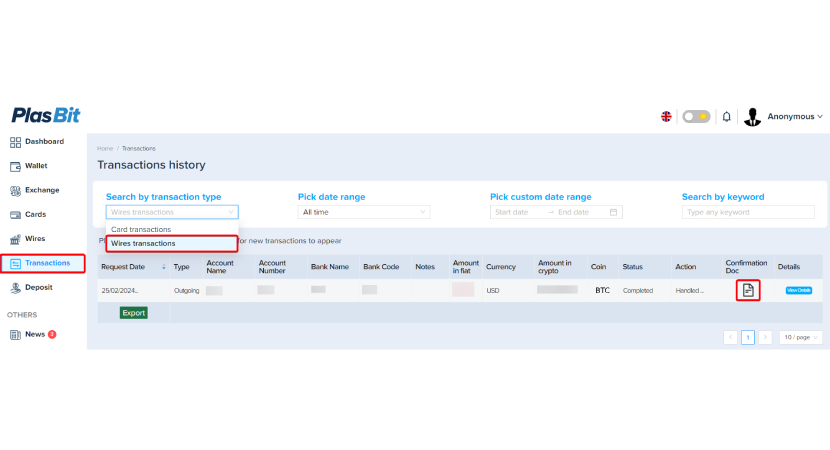
Step 12. You can check your transaction's status in the [Transactions]/[Wires transaction] selection, where you can also download a PDF confirmation once the transaction is complete.

How we got to safer markets—The early days of selling crypto
As you can see, there are plenty of options to sell and exchange cryptocurrencies that you can use at your convenience.
But it wasn't always like this. While the transactions themselves are safe due to the nature of blockchain technology, there were some severe scandals affecting cryptocurrency platforms, one of the recent ones being the FTX.
But, we will take you back to the early days of crypto exchanges to help you understand how it all began and why the first extensive exchange collapsed— enter the Mt. Gox case.
The first crypto transaction
We have all heard about the famous Satoshi Nakamoto, the father of bitcoin. But, what is lesser known is that he wasn't working on the source code alone. One of the people he collaborated with on the project was a programmer from Finland, Martii Malmi, also known as Sirius.
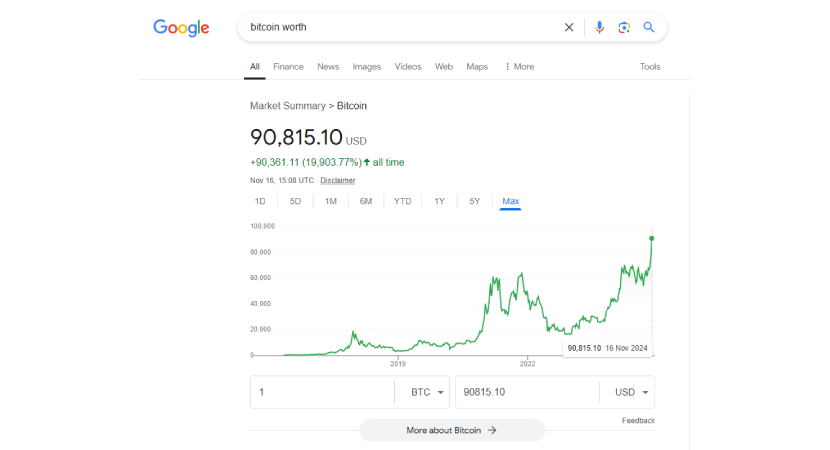
Not only did Sirius work on the most famous crypto project of all time, but he also made the first-ever BTC to USD transaction in 2009. Marti used his PayPal account to complete the transaction. Back then, he sold 5,050 BTC for $5.02. Because bitcoin had no market value then, an approximation of the electricity used to mine that amount served as the price. Interestingly, that transaction today would be worth $460,472.53.
Today, even a simple Google query shows BTC market value:
First exchange platforms
The following year, in 2010, the first official Bitcoin exchange was launched and was called BitcoinMarket. Its users primarily use PayPal to transact. However, after fraudsters exploited its chargeback policy to reverse the payments after receiving BTC, PayPal soon banned Bitcoin transactions. That effectively caused BitcoinMarket to cease its operations in 2011.
However, the major player in the crypto exchange world launched its service in 2010, Mt. Gox. Upon launch in 2006, the site was intended to be an exchange for Magic The Gathering: Online video game but was converted to a bitcoin exchange and market in 2010.
Fast forward to 2014. and Mt. Gox handled around 70% of all BTC transactions in the entire world.
Mt. Gox early issues
Problems with Mt. Gox started almost immediately. In mid-2011. as many as 25,000 BTC were stolen, affecting close to 500 accounts. To make things worse, the leaked database was put up for sale on black markets, further jeopardizing users' privacy.
Later the same year, a weakness in the Mt. Gox protocol caused 2600 more BTC to be permanently lost, as the transactions went through without a private key assigned to them, unnoticed by the network nodes. These were the early warning signs of a poorly run, unsecured system, which unfortunately didn't get the required attention.
But, the real problem happened in 2014 when the famous Mt. Gox heist happened, which affects the Bitcoin world even today.
The heist
In February 2014, Mt. Gox suspended transfers due to "suspicious activity". What first looked like a bug on the platform, as customers reported issues when trying to withdraw Bitcoin from their accounts, turned out to be a major disaster.
That suspicious activity was the biggest BTC heist, as 600-850k (!) Bitcoins were reported missing from users' accounts (only around 200k were found and returned to accounts).
Mt. Gox blamed the Bitcoin infrastructure for the issue, claiming that the faulty technology allowed hackers to change transaction IDs and steal. However, shortly after, they closed the entire website, displaying that it would be unavailable indefinitely, creating panic among users and the crypto community.
Because the stolen Bitcoins' worth was more than 450 million dollars, Mt. Gox filed for bankruptcy shortly after the heist.
Unfortunately, the scandal shook up the entire community. Investors and consumers became hesitant and no longer trusted crypto transactions as safe, which resulted in a bear market that lasted until the end of 2015.
The aftermath—Tighter regulations on crypto transactions
The early days of crypto, indeed, were anonymous, as most users were able to transact under pseudonyms. The identity verification was minimal, if present.
The Mt. Gox heist disrupted the entire market, but it went beyond that—governments and users realized that cryptocurrency transactions need to be regulated.
The direct consequence of Mt. Gox issues (but also the fact that cryptocurrencies were used for transacting illegal goods and money laundering) was the introduction of the AML (anti-money-laundering) and KYC (know-your-customer) procedures.
Japan was the first to react, as Mt. Gox was in their jurisdiction. In 2017, they released the Payment Services Act (PSA), which recognized cryptocurrencies and digital assets as legitimate property. The regulations enforced on crypto transactions are the same checks and validations that bank transactions go through. It raised cybersecurity measures, introduced KYC procedures, and implemented a crypto exchange registry.
Nowadays, most major crypto platforms and exchanges require KYC validation, and PlasBit is no exception. While this means that crypto transactions are no longer as anonymous as they used to be, ordinary users benefit from an extra layer of security the AML/KYC procedures offer, making it far less likely that a theft as significant as Mt. Gox can happen.
Cryptocurrency exchange—then and now
As you can see, the world of crypto trading has gone a long way. The early era, dating before the Mt. Gox crash, primarily relied on small markets and was unregulated. While this allowed anonymity, one of the primary reasons Bitcoin was the currency used on the Silk Road black market, numerous frauds, hacks, and security issues branded the entire crypto world as shady.
Even though the Mt. Gox catastrophe further jeopardized the reputation of cryptocurrencies, the fact that states started regulating the industry changed it forever and for good. While the government will hardly ever stop Bitcoin, some regulation was necessary.
Even if some governments ban Bitcoin or criminalize its use, it will be impossible to completely cut it out because of its decentralized nature.
Today, it is much harder to make anonymous transactions unless you do so using P2P or ATMs. However, the level of security of cryptocurrency transactions is incomparable to the early days, which is one of the reasons for the rise in market value. In fact, Bitcoin is listed on Nasdaq, which would be next to impossible if the regulations didn't step into the cryptocurrency market.
Conclusion
In this post, we explained what are the fees of selling crypto to a bank account (1% using PlasBit), explained how to do it, and also why every central platform has implemented a KYC procedure by giving you the Mt. Gox example and the heist that led to it.
As you can see, cryptocurrency trading has come a long way and is no longer reserved only for speculative and shady transactions. Nowadays, you have many safe ways to sell crypto, and using your bank account is one of them. PlasBit is no exception—we also have AML and KYC measures, and we emphasize security, all to ensure that all of the transactions remain as safe as possible and users are protected.







