Cryptocurrencies have become established investment instruments; like any other type of investment, there may come a time when you want to convert them into cash. So, what is the cost to sell crypto through bank transfer? There is a 1% fee to transfer funds from your wallet to your bank account, and the transfer usually happens on the same day but can take up to one business day, keep in mind you need to go through a KYC process before you can start the process. In this article, we'll show you how and other ways to sell your crypto for cash.
How to transfer funds from your crypto wallet
Before discussing the cost to sell crypto through bank transfer, we need to discuss complying with regulations. Irrespective of where you have your bank account, some financial regulations come into play when you transfer funds from your crypto wallet into your bank account. Plasbit requires a KYC (Know Your Customer), a process that verifies your identity. It is the primary step in complying with regulations. These are the steps to transfer funds from your wallet to your bank account. Any mention of Bitcoin applies to any other cryptocurrency supported by PlasBit.
Step 1 – Go into the wallet section
Log in to your PlasBit account and click the [Wallet] tab.
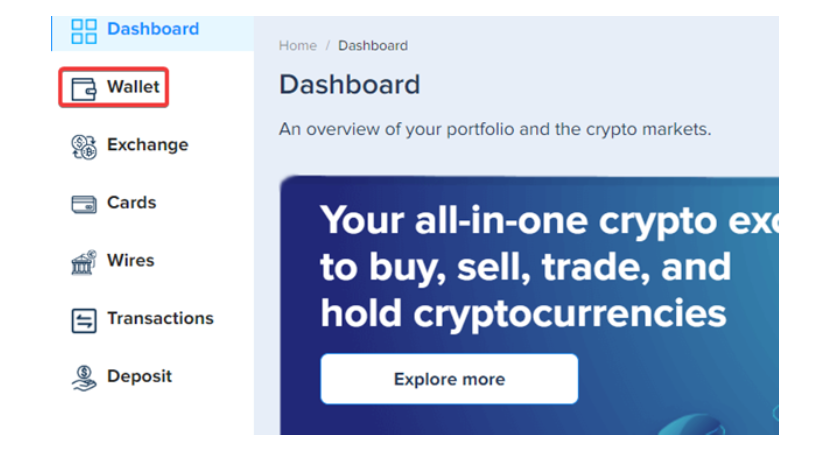
Step 2 – Deposit Bitcoin into your PlasBit wallet.
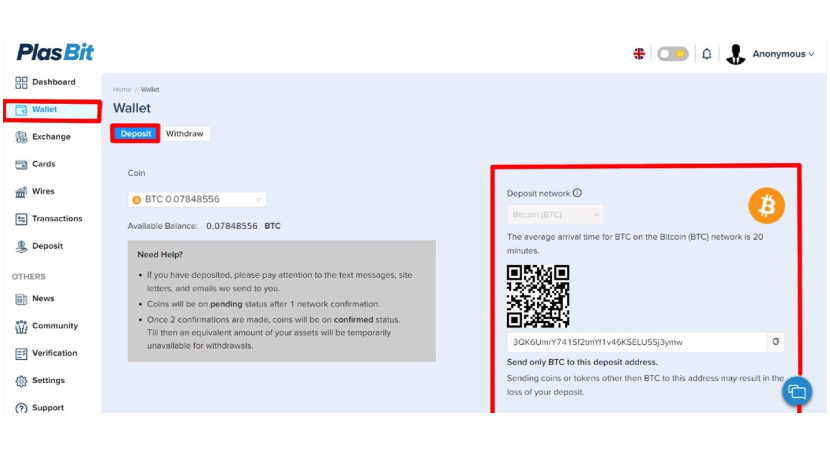
Step 3 – Click on the [Wires] Tab
Once the Bitcoin has been deposited to your wallet, click the [Wires] tab.
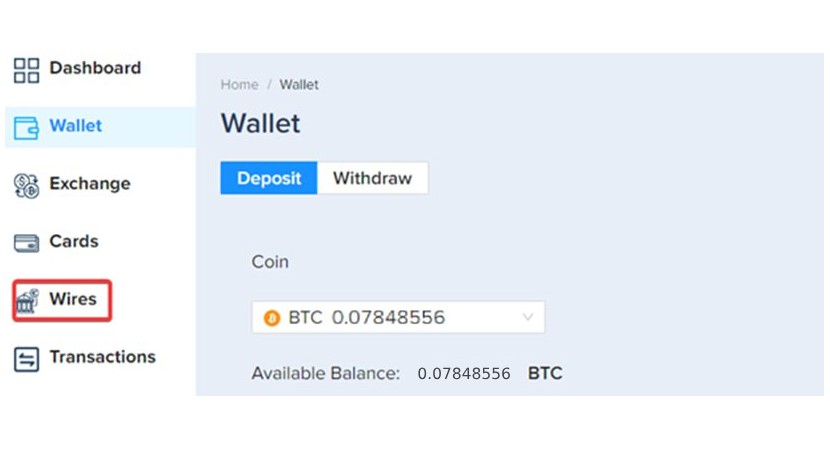
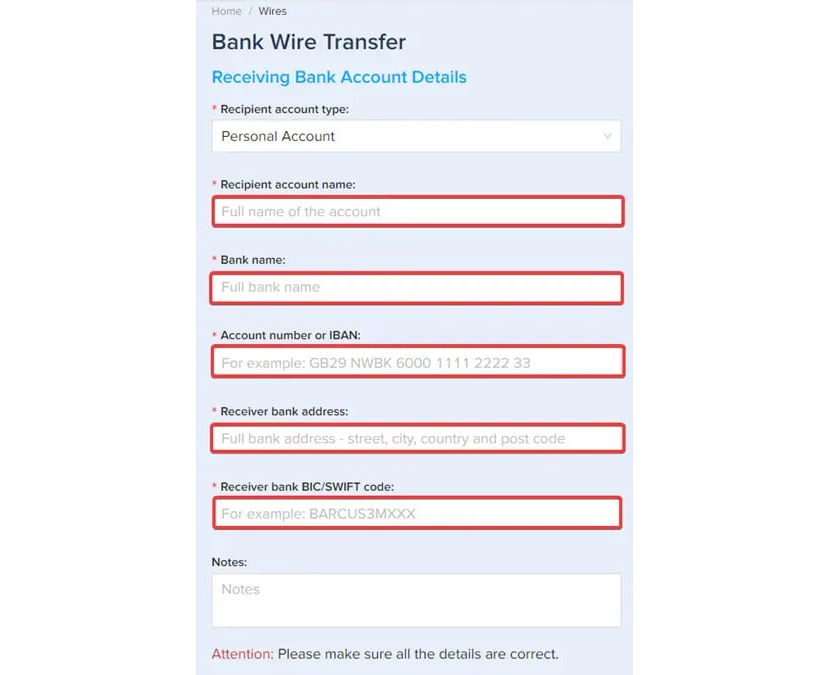
Step 4 – Bank account details
Enter your receiving bank account details. Please ensure that the account's name matches your PlasBit account's name.
Step 5 – Choose a wallet
Choose the BTC wallet from the list of wallets
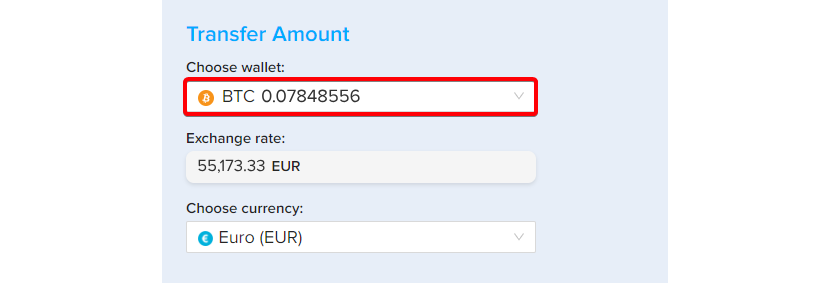
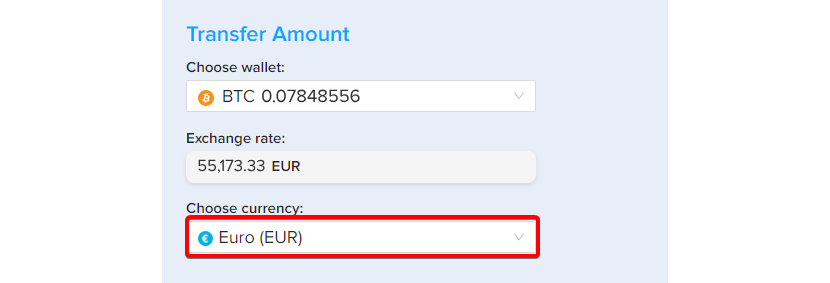
Step 6 – Select currency
Select the Euro (EUR) as the chosen currency.
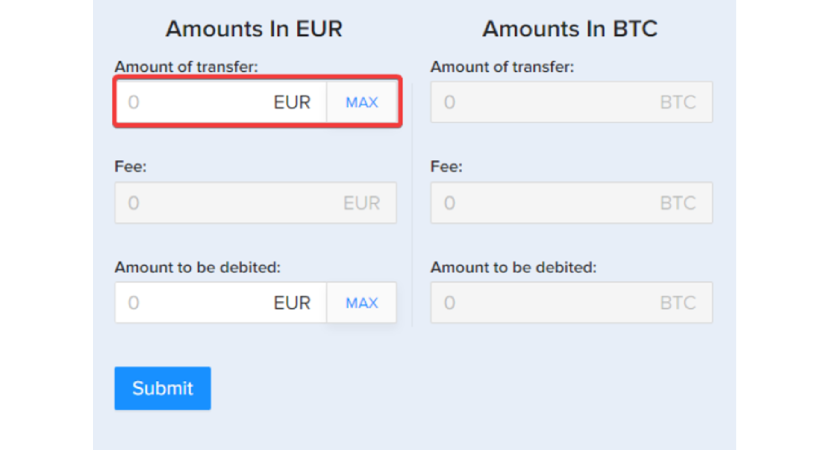
Step 7 – Amount to transfer
You can enter the amount you want to transfer to your account, and the fees will be added automatically once you have filled the "Amount of transfer" field.
You can also enter the total amount you wish to be debited from your wallet, and we will deduct the fees if you fill in the "Amount to be debited" field.
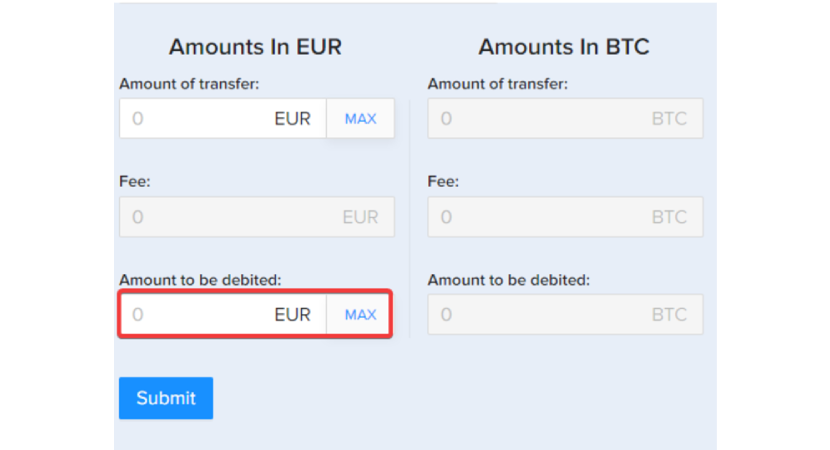
Then, click the [Submit] button. *Important – Please note that you must complete your identity verification first. Otherwise, you will not be able to process the wire request.
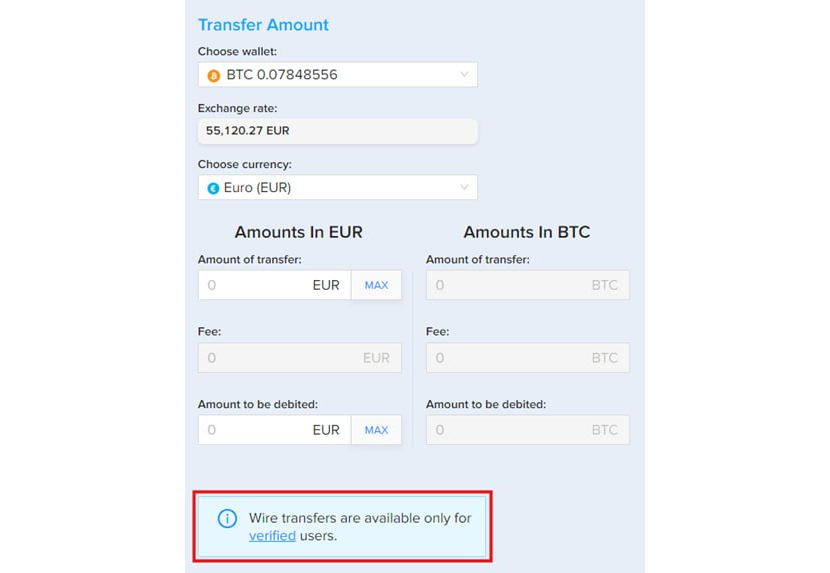
Step 8 – Check Details
Go over the wire request details and make sure everything is correct, then click [Submit]
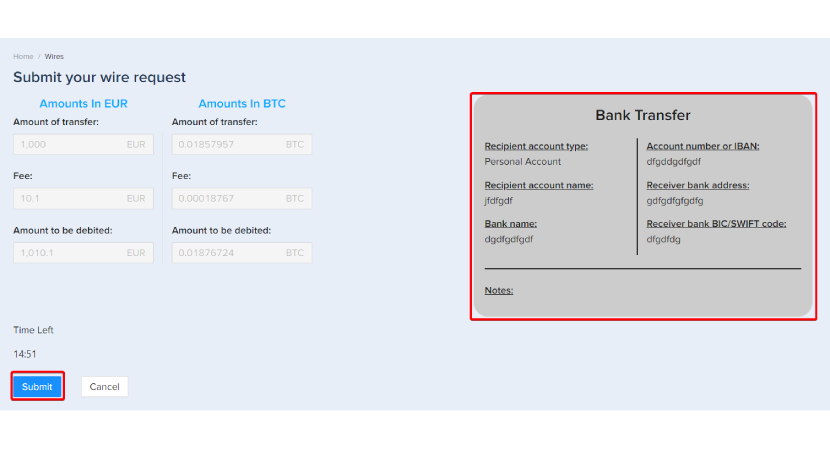
Step 9 – Security verification
Please click the [Send] button in the security verification section to receive verification codes to your phone and email.
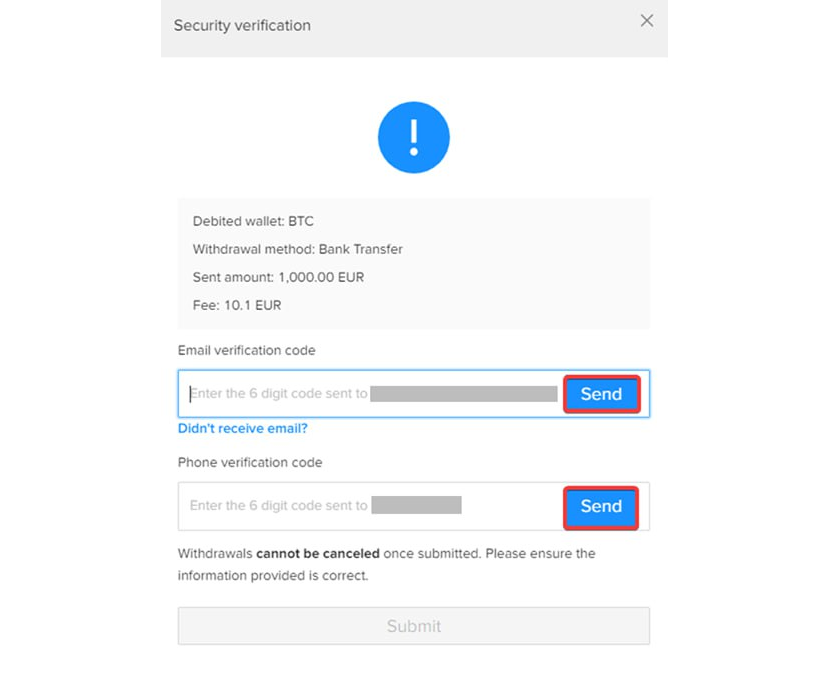
Step 10 – Verification codes
Input both verification codes, then click [Submit] to complete the wire transfer request.
Step 11 – Automatic redirection to your dashboard
You will be automatically redirected to your dashboard and immediately receive an email verifying "Wire Request Submitted."
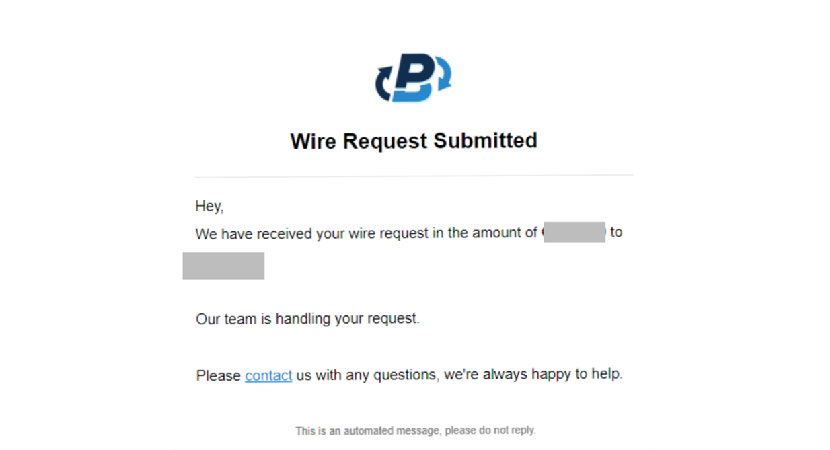
After we approve the request from our side, you will get another email that says "Wire Request Approved."

Usually, the transfer completion time is 0-1 business days.
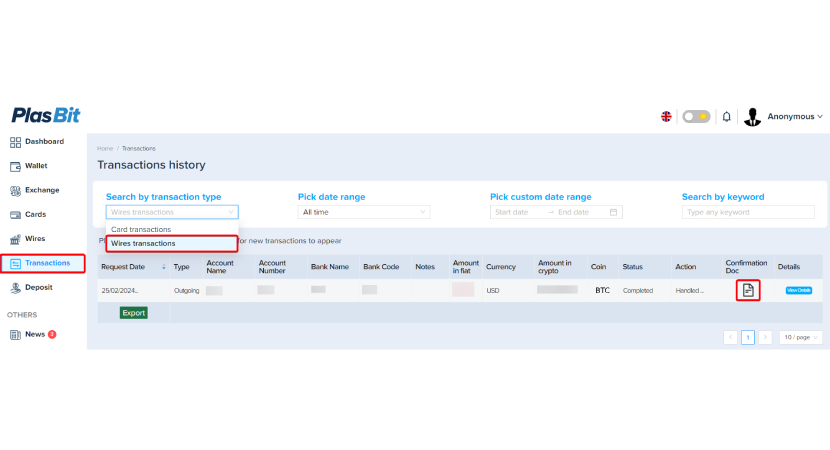
Step 12. Monitor the transfer process.
To monitor your transfer process, enter the [Transactions] section and select [Wires transaction] from the drop-down menu. Once the transaction has been approved, you can also download the Bank wire PDF.
Other ways to cash your crypto
ATMs
There are ATMs where you can turn your Bitcoin into cash. However, not every ATM supports selling (some only allow you to buy crypto with cash). You can use the internet to locate a nearby ATM that will enable you to sell Bitcoins. Once you have found it, there are several steps to follow:
· Initiate the process - Select the "Withdraw Cash" or "Sell" option on the ATM screen and specify the amount you want to withdraw.
· Get the ATM's wallet address - The machine will display a QR code representing its Bitcoin address.
· Send Bitcoin to the ATM - Using your Bitcoin wallet, scan the QR code and send the exact amount of Bitcoin specified by the ATM.
· Wait for Confirmation - The ATM will wait for the transaction to be confirmed on the blockchain, which usually takes a few minutes.
· Collect your cash - Once confirmed, the ATM will dispense the cash. You may need to verify your identity with a legal ID (driver's license, passport, etc.), and there may be a time limit (e.g., 45 minutes) to complete the transaction.
Fees
Bitcoin ATM fees typically range from 6% to 25% of the transaction amount, most falling between 10% and 20%. These fees can vary based on ATM Operator, transaction size, location, and market condition; volatility in the cryptocurrency market can affect fees. Some ATMs apply a markup to the current Bitcoin exchange rate. Users may also encounter network fees Operators justify the higher fees for Bitcoin ATMs due to costs associated with maintaining the machines, regulatory compliance, and the convenience and relative anonymity they provide.
Risks
Fraud, scams, lack of customer support, unsafe locations, unlicensed operators, and a lack of regulatory oversight are the main risks associated with using an ATM to convert crypto into cash. Inconsistent regulations across jurisdictions can lead to inadequate identity verification, making it easier for criminals to conduct anonymous transactions. The cash-to-crypto industry, dominated by crypto ATMs, has processed at least $160 million in illicit volumes since 2019, with a higher rate of illegal activity than the overall crypto industry. Also, crypto-to-cash, again using crypto ATMs, has been used to convert Bitcoin received for payment of transactions in the dark web into cash, facilitating money laundering.
Debit Cards
Using crypto debit cards provides a convenient way to access and spend crypto in everyday transactions while converting it into cash when needed at a regular ATM. A crypto debit card can be used for regular purchases or taking cash out of an ATM; however, the cost of converting everything into cash is higher than a transfer to your bank account.
Fees
There is a card issuance fee and a fee (5%) to load your card from the crypto you hold in your wallet. Using a crypto-based credit card may also incur other costs. Such as:
· Conversion fees, i.e., loading the card from crypto into your wallet.
· ATM Fees: some ATMs charge a fee to withdraw cash from a card not issued by one of the national banks.
· Network Fees: Paid for transactions to transfer crypto to the wallet.
· Foreign Transaction Fees: An exchange fee will be charged if you withdraw cash in a different currency than the one loaded onto your card.
· Card issuance fees: There is a cost associated with issuing a Crypto Card (valid for 3 years)
· Monthly fees: You pay a monthly fee to use the card; some card providers charge an inactivity fee if the card is unused for a certain period.
P2P
P2P (Peer-to-Peer) crypto exchanges facilitate direct transactions between buyers and sellers of cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. They function like a matchmaking system, connecting buyers and sellers for potential trades. Users can browse listings or create advertisements to buy or sell cryptocurrencies. When users place a buy or sell order, the platform matches them with a suitable counterparty. Once a match is found, the transaction process begins:
· The seller's cryptocurrency is held in escrow by the platform.
· The buyer transfers the agreed-upon payment to the seller using the specified payment method.
· After the seller confirms receipt of payment, the platform releases the cryptocurrency from escrow to the buyer's wallet. P2P exchanges often utilize smart contracts to automate the trading process. These contracts execute themselves when predefined conditions are met, ensuring a timely transfer of funds. Transactions are recorded on the blockchain, providing transparency and immutability. P2P platforms implement an escrow service to enhance security and build trust to protect both parties from fraud. User ratings and feedback systems are used to establish reputation. Fee structures can vary significantly between platforms, and users need to review each exchange's specific policies and potential additional costs related to payment methods or other services.
Centralized crypto exchanges
Cashing out crypto using centralized crypto exchanges is a straightforward process once you have selected a reputable centralized exchange that supports crypto and offers fiat currency withdrawals. You must check the exchange's daily, weekly, or monthly withdrawal limits. The fund typically takes one to three business days to appear in your bank account. It is advisable to enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for added security.
Fees
It's essential to review the fee structure of your chosen exchange carefully, as fees can significantly impact your overall returns, especially for more significant transactions or frequent trading. When cashing out crypto using a centralized exchange, you'll typically encounter several types of fees:
· Trading Fees - Centralized exchanges often use a tiered fee structure based on your 30-day trading volume. Higher trading volumes generally result in lower fees. Some exchanges may also offer discounts for using native tokens to pay fees. For example, up to $10K, they may charge 0.60%, reduced to 0.20% if your trading volume is between $100K and $1M.
· Withdrawal Fees - You'll likely incur withdrawal fees when moving funds off the exchange. These can vary significantly depending on the cryptocurrency and the exchange.
· Spread - Exchanges often include a spread in the quoted price when buying or selling cryptocurrencies.
· Currency conversion fees - If you convert to a fiat currency not directly supported by the exchange, you may incur additional conversion fees.
· Payment Method Fees - Additional fees may apply depending on how you cash out (e.g., bank transfer, credit card).
The early history of cashing Bitcoin
On October 5, 2009, the New Liberty Standard, a Bitcoin buying and selling service, established the first value for a Bitcoin $1=BTC 1,309.03. The value was based on the energy cost of mining Bitcoin according to the price of electricity at the time. A week later, Liberty Standard bought a total of 5.050 BTC for $5.02 through PayPal from a Finnish computer scientist and Bitcoin developer, Marttii Malmi. In February 2010, a Bitcointalk user created a portal called Bitcoin Market, where Bitcoin could be bought and sold on a P2P basis using PayPal as a payment system. PayPal withdrew its support in June 2011 due to fraud; some users stated they had received nothing in exchange for what they had paid for Bitcoins. The first reference to the creation of the first exchange, Mt.Gox, appeared on Bitcointalk on July 18 2010. It is the first time a platform reported the highest and lowest value in the last 24 hours, the volume of trading in the last 24 hours, and the highest selling and lowest buying positions in the last 24 hours. Mt.Gox is considered the first crypto exchange. It became one of the most important until 2014, when it closed following a hack and the disappearance of all the users' Bitcoins. Three new exchanges appear a few weeks after Mt. Gox's announcement, allowing exchange in fiat currencies other than the US Dollar. Britcoin exchanged Bitcoin for GBP (British Pounds), Bitcoin Brazil services exchanged Bitcoin for BRL (Brazil Reals), and BitMarket.eu exchanging Bitcoin for EUR (Euros).
The Hacks
Unfortunately, early exchanges were also victims of attacks. Hackers stole Bitcoin, user email accounts, and other details and compromised usernames. The following list is a non-comprehensive summary of the hacks against Bitcoin in the early years:
- Mt.Gox: On June 19, 2011, unknown attackers forced a security breach, stole thousands of Bitcoins from users, and compromised usernames and email accounts. Other attacks led to the closure of Mt.Gox in 2014.
- Bitomat: An important Polish exchange that became the third in volume suffers an attack, and 17,000 BTC are stolen from users.
- MyBitcoin: About 120,000 Bitcoins were stolen from users, equivalent to two million dollars at the time.
- TradeHill: Close to $ 100,000 was lost, causing the immediate closing of the exchange house, which in February 2012 had the second-highest volume.
- Bitcoinica: On May 11, 2012, he suffered the theft of 18,000 BTC, equivalent to $ 90,000.

Types of modern crypto exchanges
Cryptocurrency exchanges can be categorized into three main types: centralized (CEX), decentralized (DEX), and hybrid exchanges. Each type offers unique benefits and drawbacks. The choice between them depends on individual preferences regarding security, control, ease of use, and privacy.
Centralized Exchanges (CEX)
Centralized exchanges act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, managing transactions on behalf of users. They hold custody of users' funds and manage private keys, which means users do not directly control their assets.
Advantages:
· User-Friendly - Generally easier to use with a more intuitive interface, making them suitable for beginners.
· High Liquidity - They offer high liquidity and faster trade execution due to centralized order matching.
Disadvantages:
· Security Risks - Being centralized, they are more susceptible to hacks and fraud
· Privacy Concerns - Users must provide personal information, which can compromise privacy. In addition to that, some people are not comfortable with someone else holding their private keys for them, which is considered far less secure. These exchanges are recognized for their extensive cryptocurrency offerings, advanced trading features, security measures, and user-friendly interfaces. They cater to new users and experienced traders by providing various services, from basic transactions to complex derivative trading options.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
DEXs enable direct trading between users without a central authority using smart contracts on the blockchain. Users retain control over their private keys and funds.
Advantages:
· Enhanced Security – There is a reduced risk of hacking since users control their funds and have exclusive ownership of their private keys.
· Privacy - Users do not need to provide personal information.
Disadvantages:
· Lower Liquidity - Typically have lower liquidity compared to CEXs, which can lead to slower trade execution
· Complexity - Often have a steeper learning curve and may not be as user-friendly as centralized exchanges.
· Gas fees – unlike CEXs, the network fees are paid from your own wallet, and sometimes, a transaction will not go through because you don’t have the native coin of the network. These exchanges are notable for their unique features, blockchain support, and the variety of tokens available for trading. They provide users with decentralized options to trade cryptocurrencies securely and efficiently.
Hybrid Exchanges
Hybrid exchanges aim to combine the benefits of both CEXs and DEXs by offering centralized functionality with decentralized security features.
Advantages:
· Balanced Approach - They provide high liquidity and fast transactions while allowing users to retain control over their private keys.
· User Experience - Often feature user-friendly interfaces similar to CEXs but with added security measures from DEXs.
Disadvantages:
· Liquidity Issues – They may still face liquidity challenges compared to centralized exchanges.
· Complexity Design – They can be less intuitive due to their dual nature, potentially complicating user experience for some traders. As the cryptocurrency market evolves, hybrid exchanges are expected to play an increasingly important role, offering a balance between security, liquidity, and user autonomy. Some centralized exchanges are moving towards a Hybrid model.
Conclusion
There are several options to cash out your crypto or other cryptocurrencies; however, the cost to sell crypto through bank transfer is lower than most of the alternatives listed above, especially if you consider that you would have to incur any other associated cost with creating a Plasbit wallet and transfer your crypto to it for all the other possible ways to cash out your cryptos. It also has one of the fastest transaction times at a high level of security. Selling crypto through bank transfers also meets all the regulations to prevent Money Laundering and the ones about properly identifying your customers.







