For a beginner, it can be challenging to understand the world of cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies, blockchains, interoperability issues, gas fees, and many other complicated points exist. In this PlasBit article, we will find out how to solve the problem that happens to many on Trust Wallet related to the "You don't have enough Arbitrum (ETH) to cover network fees" pop-up when you try to withdraw Arbitrum (ARB). We have discovered that the main problem is that you need to have ETH coins on the Arbitrum One network so you can proceed with the ARB transfer. This guide will explore three options to solve your problem and transfer money from your crypto wallet.
Problem: You Don't Have Enough Arbitrum (ETH) To Cover Network Fees
Let us understand the problem together. You want to proceed to transfer Arbitrum (ARB) from your Trust Wallet, but you cannot complete it because an error message appears. Why? And what should you do to solve it? This is because Arbitrum is an Ethereum Layer 2 blockchain. Carrying out transactions requires a gas fee in ETH, which must have been previously deposited on the Arbitrum One Network. So, if you see this error, it's because you don't have enough Arbitrum (ETH) to cover network fees. This is the main problem, but why is a gas fee needed?
How Gas Fees Work?
In the context of blockchain, "gas" refers to the computational effort required to execute operations or smart contracts on the network. Users attach a specified amount of cryptocurrency as gas to their transactions, indicating the maximum fee they are willing to pay for the computational resources required. Miners or validators prioritize transactions based on the associated gas fees, with higher fees often leading to faster processing. Gas fees are an economic mechanism that encourages efficient resource allocation and discourages network congestion. Essentially, they ensure that the blockchain operates smoothly and that participants are appropriately incentivized for their computational efforts in maintaining the integrity and security of the network.
Why Do I Have to Pay the Gas Fee in ETH?
On Arbitrum and other Layer 2 solutions, transactions often settle on Ethereum (ETH); therefore, gas fees must be paid in ETH. Arbitrum is a Layer 2 scaling solution built on the Ethereum blockchain to provide faster and more cost-effective transactions. However, it relies on the security and decentralization of the Ethereum mainnet.
Even though transactions on Arbitrum occur on Layer 2, they still interact with the Ethereum mainnet to ensure security and distributed consensus. As a result, gas fees for transaction execution and security must be paid in ETH, the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain. This approach allows for the speed and efficiency gains of Layer 2 solutions while maintaining the security and trust provided by the Ethereum mainnet.
Step-By-Step Guide to Withdraw ARB from Trust Wallet
In cryptocurrencies and blockchain, clear and specific guides are needed. That is why, at PlasBit, we have analyzed this common problem and provided a step-by-step guide with different solutions depending on your preferences and needs.
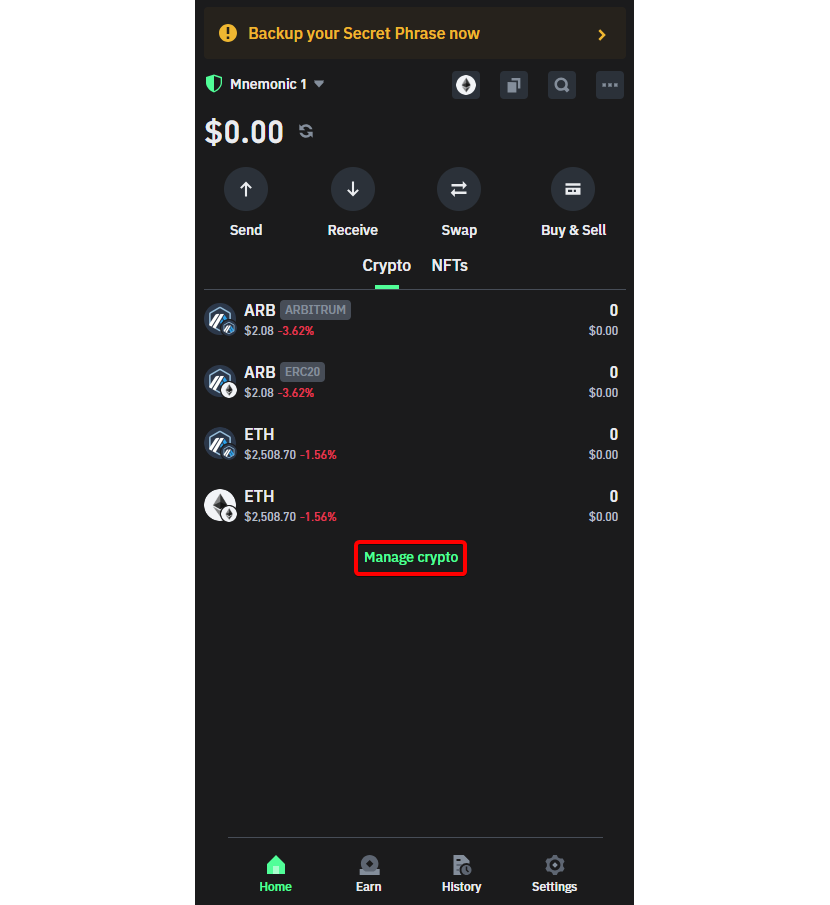
Step 1: Manage your Crypto to Ensure Compatibility
On Trust Wallet, you must add this cryptocurrency before getting the ETH you need to transact on the Arbitrum One network. So, first, go to 'Manage Crypto' to activate the ETH wallet on the Arbitrum One network.
Step 2: Search and Activate your ETH on Arbitrum Network
You can easily find the ETH cryptocurrency on the Arbitrum network by searching for' ETH' in the search bar. Click on the button to add it to proceed to the next step.
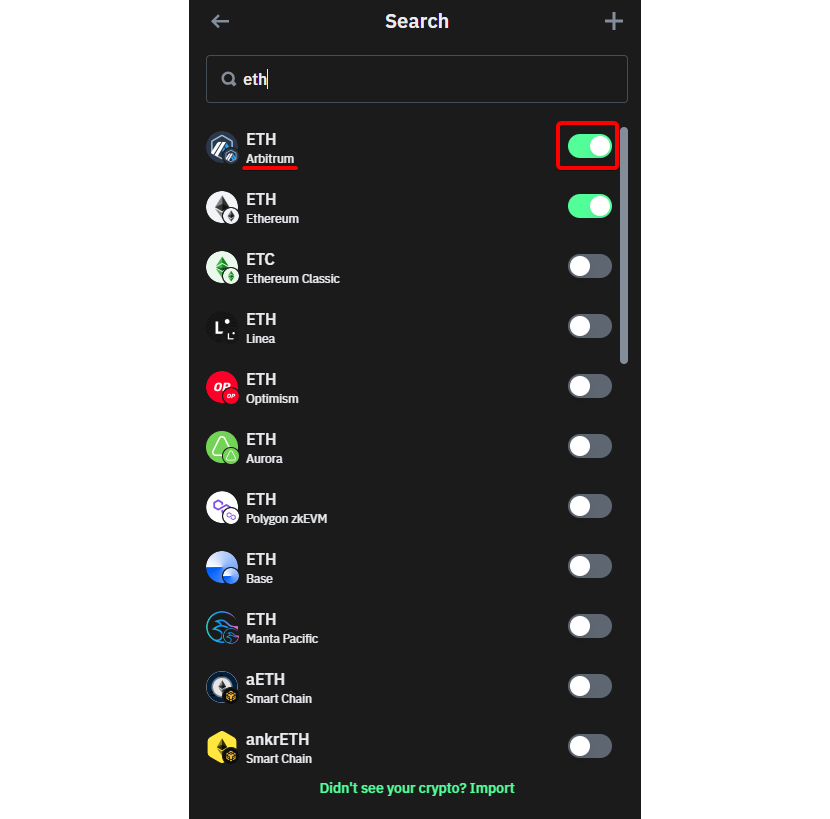
These preliminary steps were indispensable to have ETH on the right network. As explained above, and as we will elaborate on later, Arbitrum is an Ethereum Layer 2 blockchain aiming to increase the main blockchain's scalability. Despite this, it still needs ETH to pay the fee to perform transactions and write to the blockchain. Thus, on Trust Wallet, having the ETH coin on an active Arbitrum network is an indispensable step to making an Arbitrum withdrawal (ARB).
Step 3: Exploring 3 Possible Solutions
Now that we have set up the wallet to be compatible with having ETH on the Arbitrum network, we have several possibilities to get it. In detail and with pictures, we will explain all three possible options you can take.
Option A: On Trust Wallet, Buy ETH on Arbitrum One
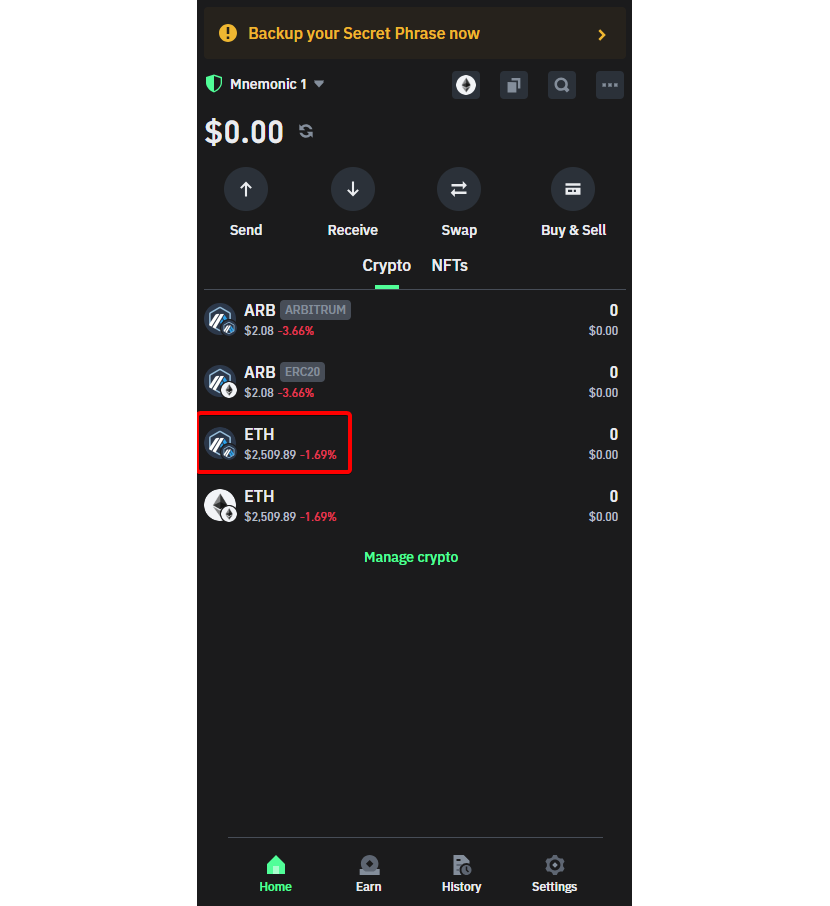
Step A-1: Click on the crypto ETH with the Arbitrum logo. Having added it previously, you can click on ETH on the Arbitrum network from the Trust Wallet home page to go to the next step.
Step A-2: Make a purchase of ETH on the Arbitrum network. Click on the "Buy" button to start the purchase process within the wallet itself.
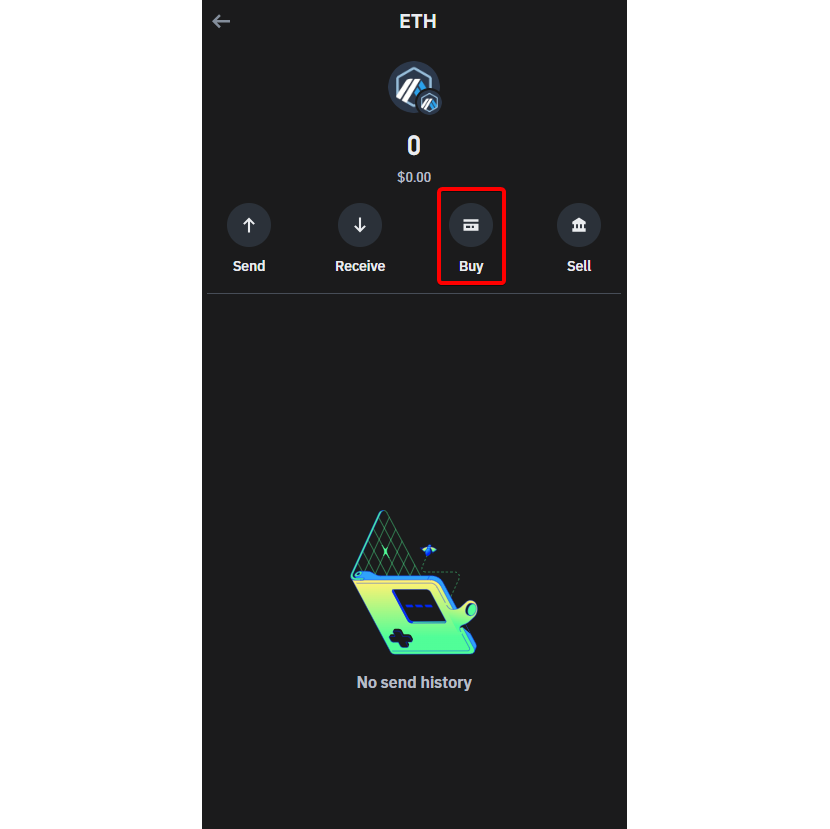
Step A-3: After clicking the "Buy" button, you will be taken to the purchase section. Here, you can choose your preferred third-party provider to make the purchase. Evaluate the different commissions and costs that may be involved to make an informed choice.
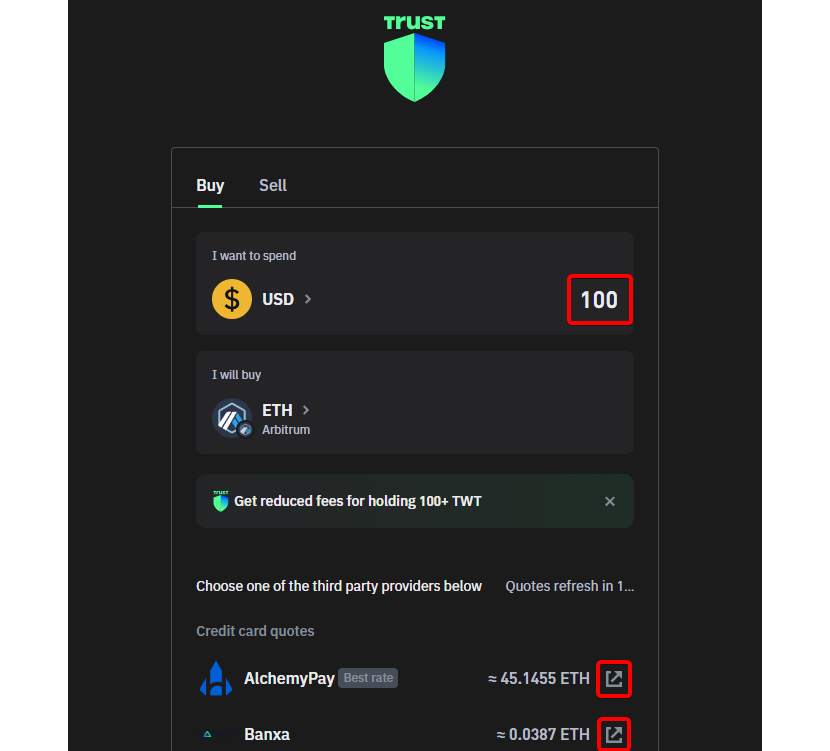
Step A-4: Buy ETH via a Third-Party Provider: After carefully evaluating costs and fees, choose the vendor that best meets your requirements and purchase it via fiat currency. However, ensure that the ETH purchased is specific to the Arbitrum One Network.
Option B: Utilizing the "Swap" Feature on Trust Wallet.
Step B-1: Open your Trust Wallet and click on 'Swap'. After going to your home page, click the swap button to swap and obtain ETH on the Arbitrum network.
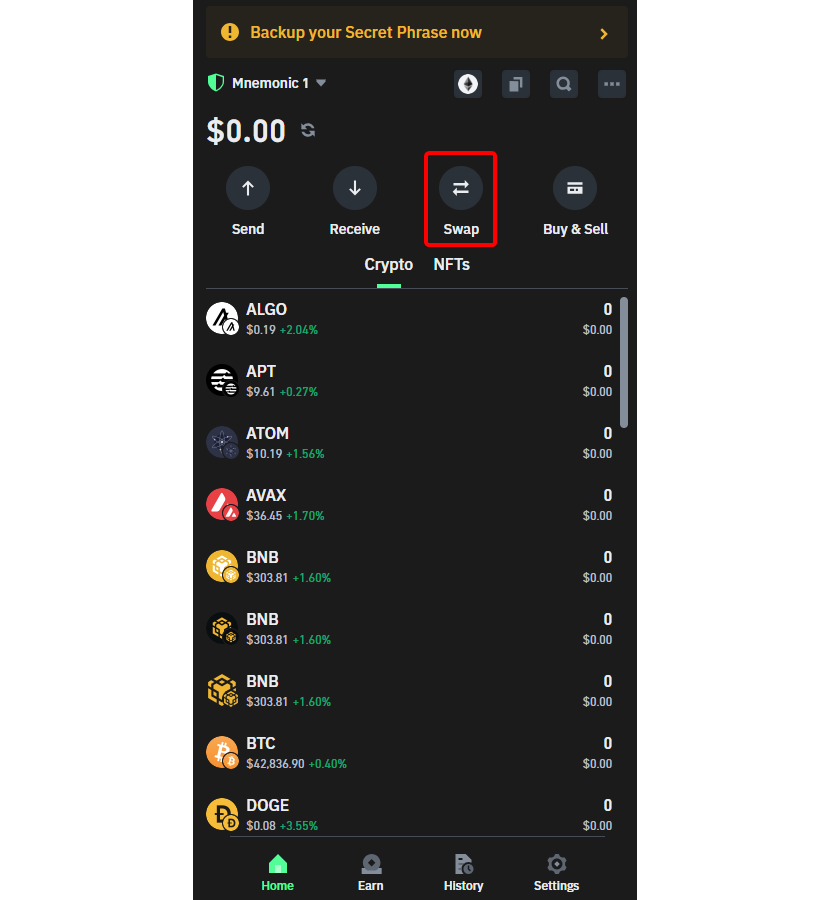
Step B-2: Choose a crypto to swap: Choose a crypto you already have in your wallet to convert to ETH on the Arbitrum network. Ensure you have the funds to do the swap and remember to choose the Arbitrum network.

Step B-3: Select the ETH crypto on the Arbitrum network and swap. Select the proper crypto on the right network, double-check the transaction to ensure everything is correct, and execute the swap.
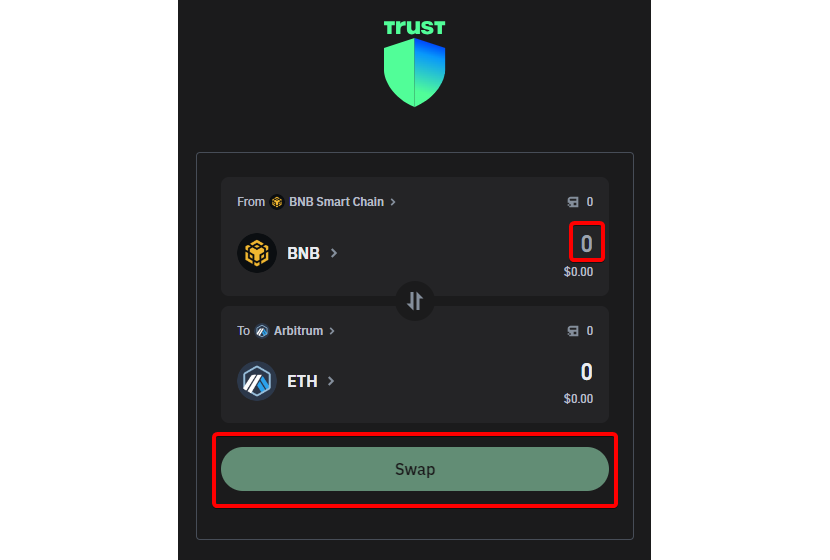
In these two ways just listed, option A and option B, you will get ETH on the Arbitrum network directly within your own Trust Wallet. But sometimes, using an external exchange to purchase may be convenient due to lower commissions and fees. In the next option, we will consider another possibility: buying ETH on Arbitrum via an external crypto exchange.
Option C: Buy on a Crypto Exchange
It is often convenient to withdraw and send ETH on the Arbitrum network from a crypto exchange. We will use our exchange as a case study in this last possibility.
Step C-1: After you have done your research to select the best exchange for your needs, proceed to sign up. Register with your email address to access the platform features, and verify your email to log in to the platform for the first time. Then, enable 2FA for increased security and prevention of attacks.
Step C-2: Go into the “Wallet” Section, and deposit funds on the exchange via cryptocurrency transfer.
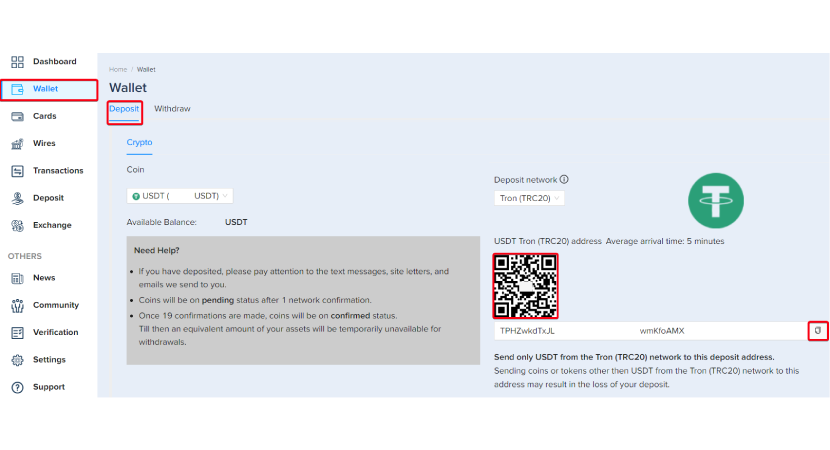
Step C-3: Click the Exchange section to convert your funds into ETH on the Arbitrum network.
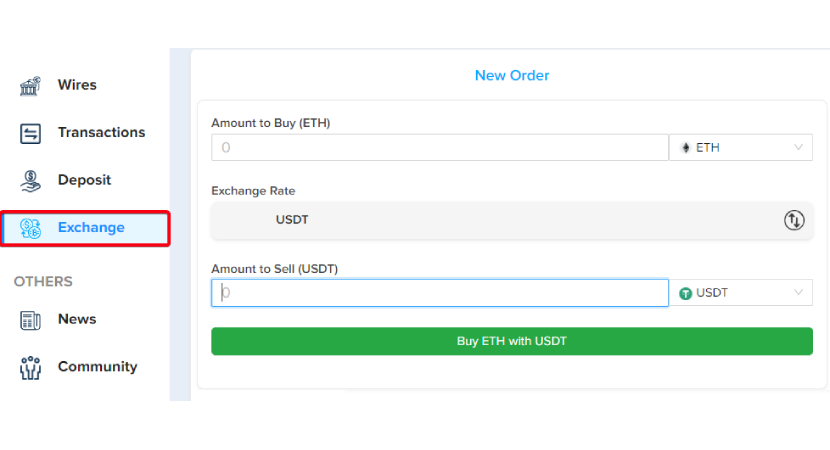
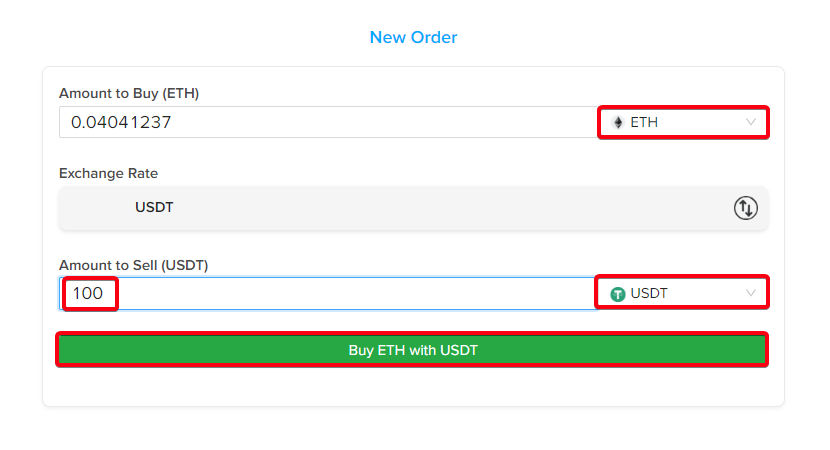
Step C-4: Convert your cryptocurrency to ETH. Be sure to check the data and select the correct cryptocurrencies for the exchange.
Step C-5: Send the acquired ETH to your address on Trust Wallet.
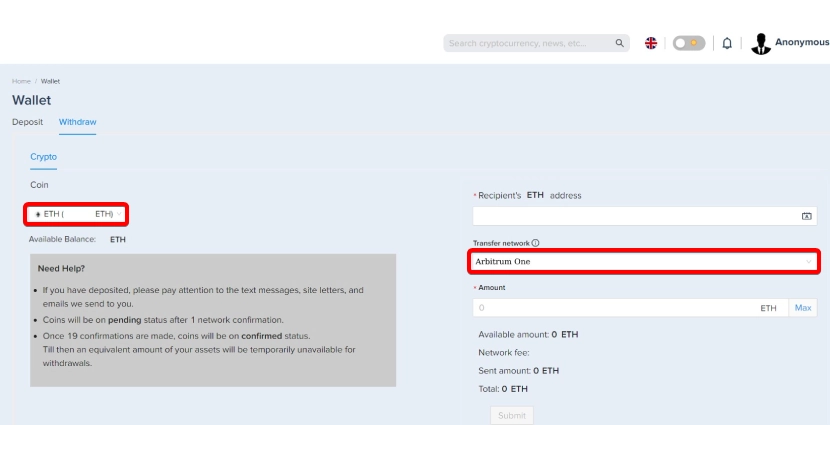
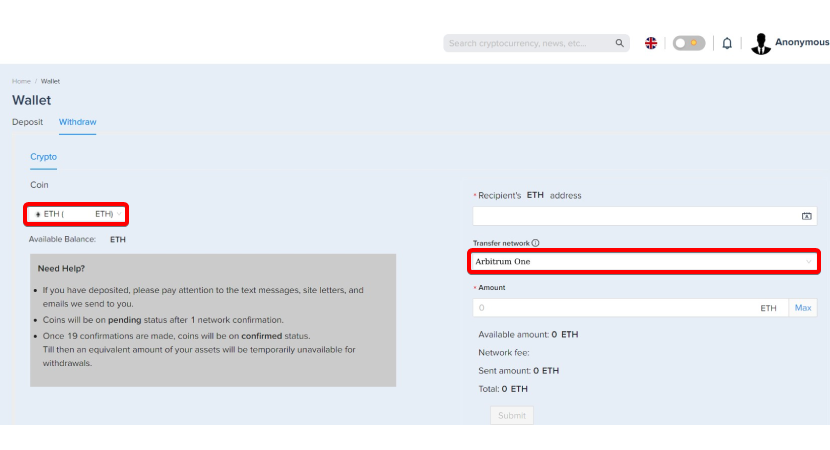
Step C-6: Withdraw your ARBs from the Trust Wallet. You now have the ETH you need to pay the gas fee.
Using one of these three options, if you do not have Arbitrum (ETH) to cover the network fees on your Trust Wallet, you can solve your problem!
Layer 2: A Closer Look to Blockchain Scaling Solutions
Layer 2 emerges as a dynamic realm strategically designed to overcome the scalability challenges deeply rooted in Layer 1 blockchains. Instead of overhauling the fundamental protocol, Layer 2, exemplified by solutions like Arbitrum, introduces inventive mechanisms operating atop blockchains. These mechanisms act as catalysts, enhancing the network's capacity to handle a growing transaction load while steadfastly preserving the principles of decentralization.
Off-Chain Scaling Techniques
A defining characteristic of Layer 2 solutions is adopting off-chain scaling techniques. State channels and sidechains, integral components of Layer 2, divert specific transactions from the main blockchain. This strategic maneuver alleviates congestion on Layer 1, paving the way for more efficient and rapid transaction processing. State channels, in particular, enable parties to engage in off-chain transactions, reducing the burden on the main blockchain and significantly enhancing overall scalability.
Smart Contracts in the Layer 2 Landscape
While smart contracts predominantly find their home in Layer 1, Layer 2 solutions introduce novel dimensions to their functionality. Some Layer 2 implementations facilitate the execution of smart contracts with reduced fees and accelerated confirmation times, seamlessly harmonizing efficiency with the foundational tenets of decentralized computation. This evolution expands the utility of smart contracts, making them more accessible and cost-effective for a broader range of applications.
Optimizing Smart Contract Execution
Layer 2 solutions, such as Optimistic Rollups, go beyond basic transaction scaling and actively optimize the execution of smart contracts. By moving specific computational processes off-chain, these solutions enhance the efficiency of decentralized applications (DApps), fostering a more seamless user experience. Optimistic Rollups, for instance, combine off-chain execution and on-chain validation, striking a balance between speed and security.
Interoperability and Layer 2 Smart Contracts
The interoperability of Layer 2 solutions is a critical aspect of their success. Ensuring that Layer 2 smart contracts can seamlessly communicate with those on Layer 1 and other Layer 2 networks is essential for the broader adoption and integration of these scaling solutions. Initiatives like cross-chain bridges enable the smooth transfer of assets and data between different layers.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While Layer 2 solutions offer promising scalability enhancements, they are not without challenges. Ensuring the security of off-chain transactions, maintaining decentralization, and addressing potential interoperability issues are vital concerns. However, ongoing research and development within the Layer 2 space and community-driven innovations paint a hopeful picture for the future. As the technology matures, Layer 2 is poised to become an integral component in the evolution of blockchain networks, providing a scalable and efficient foundation for decentralized applications.
Understanding Arbitrum: Scaling Ethereum with Confidence
Arbitrum is a pioneering technology suite designed to address the scalability limitations of Ethereum. In this chapter, we'll delve into how Arbitrum operates, its key features, and the components that make it a powerful scaling solution.
How Blockchain Transactions Work?
Transactions on the blockchain are processes of exchanging digital values recorded permanently and immutably on a chain of blocks. When a user initiates a transaction on Arbitrum One, it is broadcast to the network, where participants (nodes) verify it through complex cryptographic algorithms. Once confirmed, the transaction is grouped with others into a block and added to the chain. This process, known as mining or validation, involves solving complex mathematical problems. Additionally, distributed consensus among participants ensures the security and integrity of the blockchain network. Transactions on the Arbitrum blockchain also involve the concept of ETH gas fees. Gas fees are the costs associated with processing and validating transactions on the network. Users include a certain amount of cryptocurrency as a gas with their transactions to incentivize miners or validators to process them.
Ethereum Compatibility
Arbitrum retains Ethereum compatibility as a paramount feature. Users can seamlessly interact with Arbitrum using their favorite Ethereum wallets, and developers can deploy smart contracts with familiar Ethereum libraries and tools. The user experience mirrors Ethereum closely, with the crucial distinction of significantly reduced transaction costs and faster processing times.
Arbitrum Rollup
Arbitrum Rollup, the flagship product, employs an Optimistic rollup protocol. It operates as a sub-module within Ethereum, alleviating the burden on Ethereum nodes by processing only a fraction of Arbitrum transactions. Ethereum adopts an "innocent until proven guilty" approach, assuming proper rules adherence initially. Any potential violation is disputed on Ethereum Layer 1, where fraud is proven or disproven, ensuring the system inherits Ethereum's robust security.
Fraud Proof Mechanism
Arbitrum's key feature is its ability to adjudicate and prove fraud on Ethereum Layer 1. In case of a dispute, validators play an interactive game, narrowing down the disagreement to a single computational step. This step is executed on Ethereum Layer 1, proving the veracity of the honest party's claims and penalizing malicious actors.
Transaction Processing
Arbitrum achieves lower transaction costs primarily through optimistic execution. While Ethereum transactions are processed individually, Arbitrum batches multiple transactions in a single submission, significantly reducing overhead costs. Additionally, transaction data is posted on Ethereum Layer 1 in compressed form, further minimizing the footprint and translating to lower transaction costs.
Withdrawal Delays
The only delay experienced by users is during the withdrawal process, where moving funds from Arbitrum back to Ethereum may require a waiting period of one week. However, utilizing fast-bridge applications can bypass this delay for a small fee. Other user actions, such as depositing funds onto Arbitrum or using dApps on an Arbitrum chain, do not incur withdrawal delays.
Arbitrum AnyTrust Chains
Arbitrum AnyTrust chains provide an alternative to Rollup chains' full decentralization and trustlessness, offering lower fees. Data management occurs off-chain, and in the event of a challenge, the chain reverts to "rollup mode." This mode assumes that at least two committee members are honest, providing a sensible tradeoff for applications prioritizing high transaction throughput over full decentralization.
Multiple Chains
Arbitrum allows the existence of multiple chains running in parallel. Currently, on the Ethereum mainnet, Arbitrum One (Rollup) and Nova (AnyTrust) cater to different security and transaction cost needs. Developers also have the option to launch their own Arbitrum chains, known as Orbit chains.
Arbitrum's innovative approach to scaling Ethereum brings a new efficiency level to the blockchain ecosystem. Whether through Rollup chains for enhanced security or AnyTrust chains for cost-effectiveness, Arbitrum offers a versatile solution that adapts to the diverse needs of users and developers, maintaining Ethereum's ethos of decentralization and accessibility.
A Brief Recap of Problem and Solutions
Navigating the world of cryptocurrencies can be challenging, especially for newcomers encountering issues like the "You don't have enough Arbitrum (ETH) to cover network fees" message on Trust Wallet. We've explored the root of this problem and provided comprehensive solutions to ensure a smooth withdrawal of Arbitrum (ARB). Let's wrap up our findings and guide in this conclusive chapter.
Understanding the Problem
The primary issue arises from the necessity of having ETH on the Arbitrum One network to cover network fees. Arbitrum, being an Ethereum Layer 2 blockchain, relies on gas fees in ETH for transaction processing. If you encounter this error, it indicates a lack of Arbitrum (ETH) to cover the required network fees.
How Blockchain Transactions Work
Before delving into solutions, it's crucial to understand how blockchain transactions operate. Transactions involve exchanging digital values, verified by participants through complex cryptographic algorithms. Gas fees, representing the computational effort required, ensure efficient resource allocation and discourage network congestion. In the blockchain, gas fees are paid in cryptocurrency to incentivize miners or validators to process transactions.
Why Pay Gas Fees in ETH
Arbitrum, as a Layer 2 scaling solution on Ethereum, settles transactions on the Ethereum mainnet. Despite operating on Layer 2, it interacts with Ethereum for security and distributed consensus. Thus, gas fees for transaction execution and security must be paid in ETH, maintaining the speed of Layer 2 while upholding the security of the Ethereum mainnet.
Step-By-Step Guide to Withdraw ARB from Trust Wallet
In response to the issue, we provided a detailed guide with three options:
- Option A: Purchase ETH on Arbitrum One directly within the Trust Wallet.
- Option B: Utilize Trust Wallet's "Swap" feature to convert an existing cryptocurrency to ETH on Arbitrum.
- Option C: Buy ETH on Arbitrum through an external crypto exchange.
Each option offers a solution tailored to user preferences, ensuring they acquire the necessary Arbitrum (ETH) to cover network fees.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of gas fees, the necessity of ETH on the Arbitrum One network, and the available solutions empowers users to navigate challenges seamlessly. PlasBit aims to provide clear and specific guidance, enabling users to address common problems effectively. As the cryptocurrency ecosystem evolves, staying informed and equipped with practical knowledge ensures a positive and secure user experience. Whether opting for in-app purchases, swaps within Trust Wallet, or external exchanges, users can now confidently resolve the "Arbitrum (ETH) to cover network fees" issue and proceed with their transactions on the Arbitrum network.







