Cryptocurrencies are complicated, and some actions or transactions often cannot be executed due to network or fee problems. If you can't withdraw Arbitrum from Trust Wallet and don’t understand why, we have the solutions. This is the step-by-step guide to fix your problem!
Our PlasBit Team, experiencing first-hand the problems associated with Arbitrum transfers from Trust Wallet, worked to explain the dynamics that do not allow for easy withdrawal. The focal issue is the necessity of having Ethereum (ETH) on the Arbitrum One network to cover transaction fees. This crucial detail should be remembered and needs to be clarified.
Why You Can't Withdraw Arbitrum From Trust Wallet ?
We’ll dissect the problem and provide a guide with 3 specific solutions to overcome withdrawal challenges on Trust Wallet, offering efficiency and simplicity for users seeking to solve the issue with Arbitrum (ARB) withdrawal.
The Problem: Missing ETH Gas Fee on Arbitrum One Network
The critical problem lies in the requirement for ETH on the Arbitrum One network. Like conventional transactions on a blockchain, withdrawing a cryptocurrency requires a gas fee. In our problem, Arbitrum tokens demand a specific amount of ETH to serve as gas fees. In fact, users are prompted with an error message when attempting withdrawals without a sufficient ETH balance on the Arbitrum One network.
What is a Gas Fee?
Gas fees are the charges users pay to execute transactions on a blockchain. Blockchains require computational resources to process and confirm transactions, and the gas fees represent the cost associated with these resources, compensating miners or validators working to ensure the security and integrity of the network.
Why Do I Have to Pay in ETH to Withdraw ARB?
In our case, if you can't withdraw Arbitrum from Trust Wallet, you need ETH on the Arbitrum One network as the gas needed to execute the transaction. But why? It’s because Arbitrum is a layer 2 blockchain, a scaling solution for Ethereum, and all Arbitrum transactions are powered by the Ethereum network.
By comprehending the fundamental elements of the withdrawal challenge, you can embark on your journey equipped with the knowledge necessary to address the issue at its core. We will delve into step-by-step solutions, ensuring you can confidently navigate the intricacies of your wallet and successfully withdraw Arbitrum.
Critical Steps for Arbitrum Withdrawals
In crypto management, continuing learning ensures an easy experience, especially when dealing with the complexities of different wallets. PlasBit will explain the steps and considerations that users should know before embarking on the withdrawal, emphasizing the significance of preparatory measures in a successful transaction.
Step 1: Ensuring Wallet Compatibility
Not all digital wallets are created equal, making compatibility a paramount consideration. Users are urged to meticulously ensure that their chosen wallet seamlessly supports the intricacies of the Arbitrum currency.
In Trust Wallet, you must activate the (ETH) wallet on the Arbitrum network. Navigating through the "manage crypto" option to ensure compatibility and support for the Arbitrum currency. This preparatory measure establishes a foundation for successful withdrawal transactions.
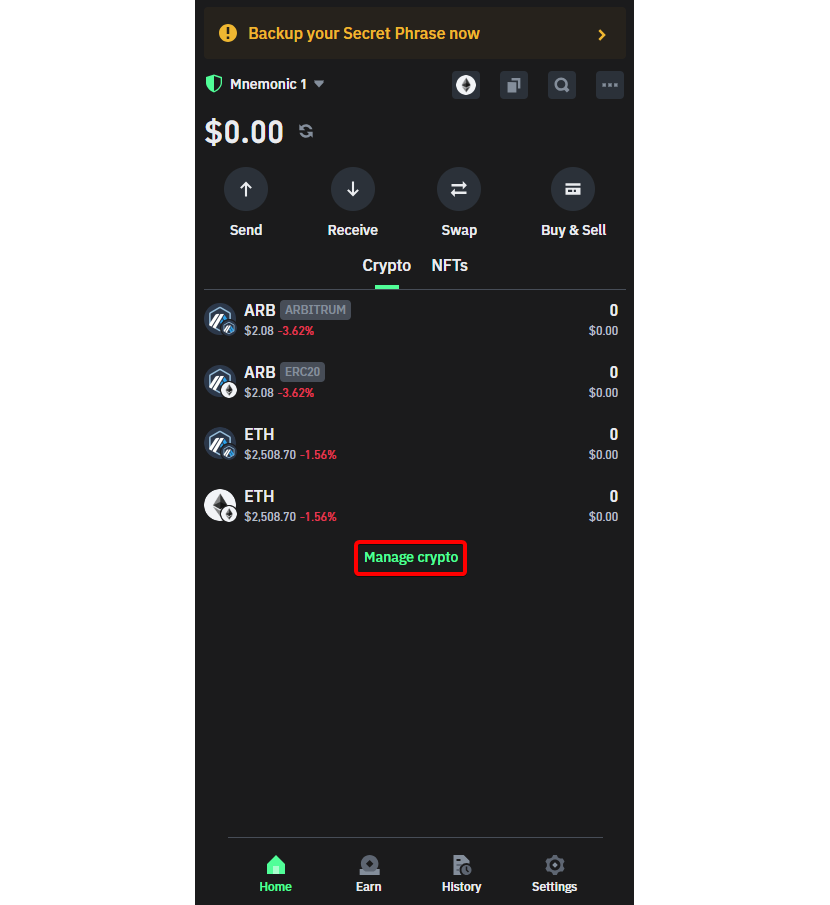
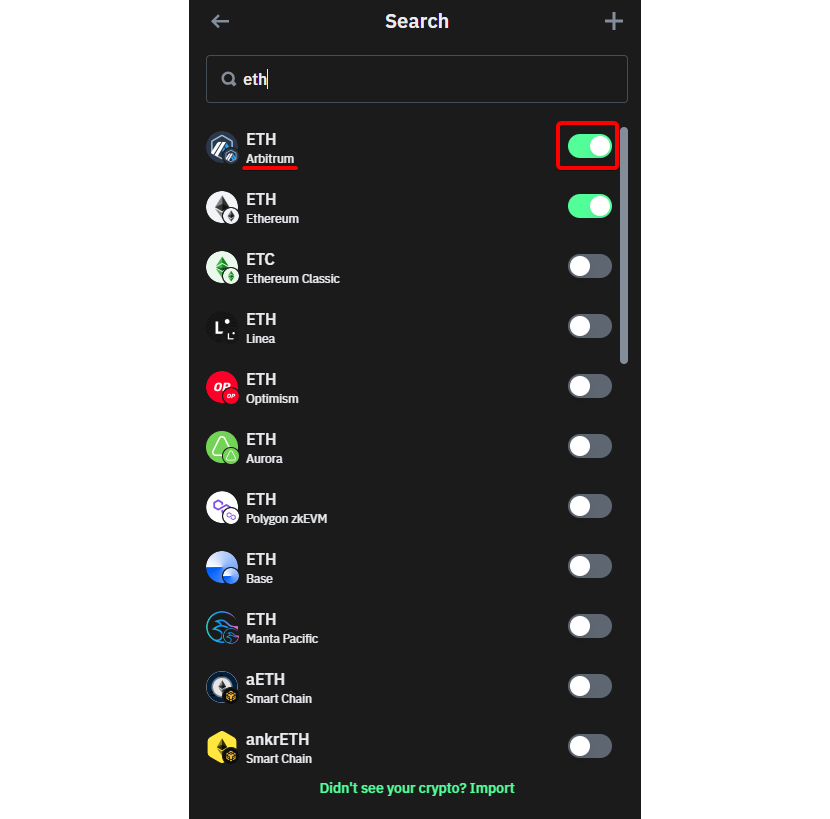
Step 2: Activating the ETH Wallet on Arbitrum
Embarking on an Arbitrum withdrawal necessitates the activation of the Ethereum (ETH) wallet on the Arbitrum network, a pivotal prerequisite for a seamless transaction. This activation lays the foundation, empowering the wallet to handle ETH and ARB transactions adeptly. As users conscientiously equip themselves with the meticulous preparations outlined in this chapter, they establish the bedrock for a correct Arbitrum withdrawal. These proactive measures elevate the likelihood of a transactional odyssey devoid of pitfalls. Subsequent chapters will serve as a comprehensive guide, steering users through diverse solutions available within your wallet and ensuring a nuanced understanding of the platform's functionalities tailored to address the unique challenges posed by Arbitrum withdrawals.
Navigating Trust Wallet: A Step-by-Step Guide to Arbitrum Withdrawals
With a solid foundation laid through critical preparations, users are now ready to embark on the practical journey of executing Arbitrum withdrawals on Trust Wallet. We will provide a comprehensive, step-by-step guide for users to navigate the platform effectively and overcome withdrawal challenges using the three proposed solutions within Trust Wallet.
Option A: Purchasing ETH on Arbitrum One Through Trust Wallet
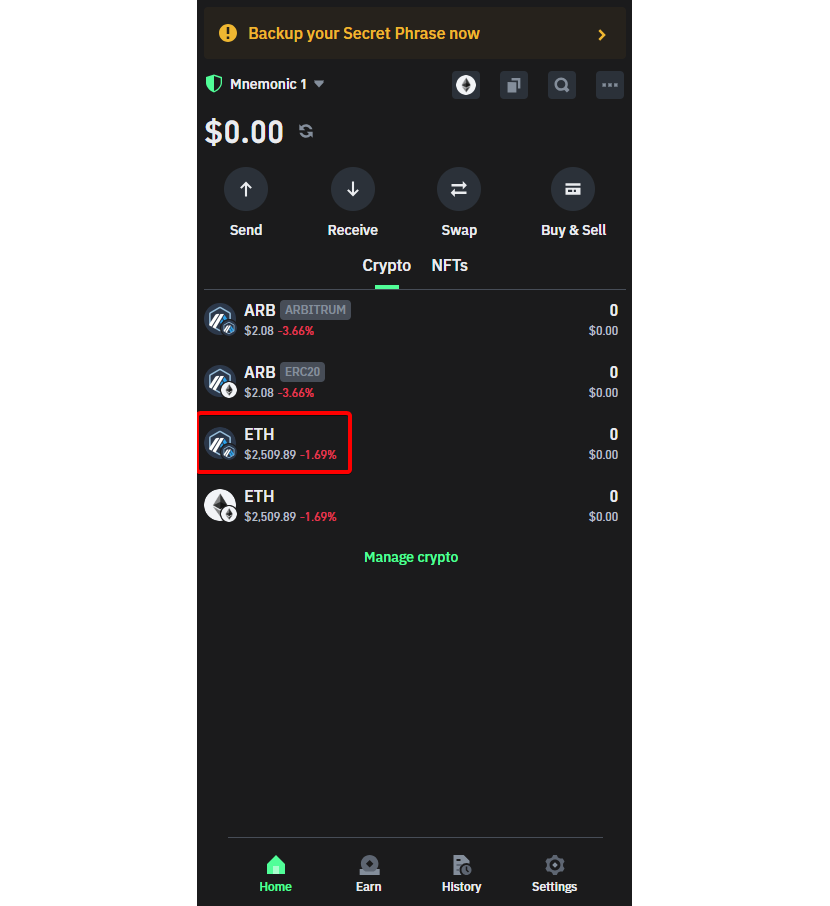
- Step 1: Accessing the ETH coin on Arbitrum Network: Open Trust Wallet and click on ETH on Arbitrum network.
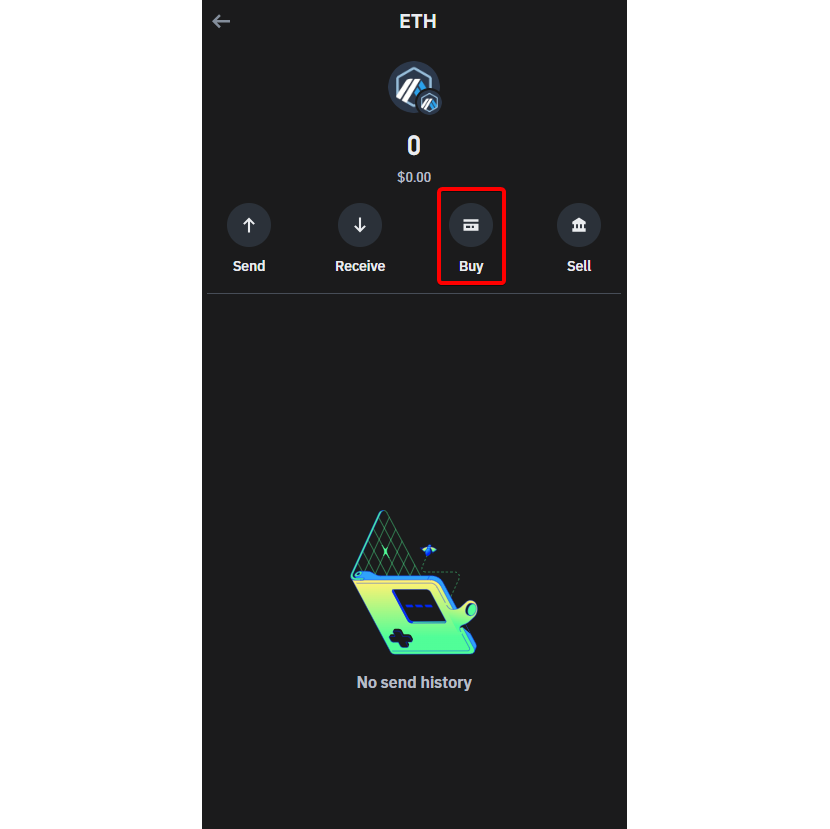
- Step 2: Starting the Purchasing: Once you are directed to the coin page, press on the “buy” option.
- Step 3: Exploring Third-Party Companies: Browse through the list of third-party companies in the "Buy" section that offer Ethereum (ETH) on the Arbitrum network.
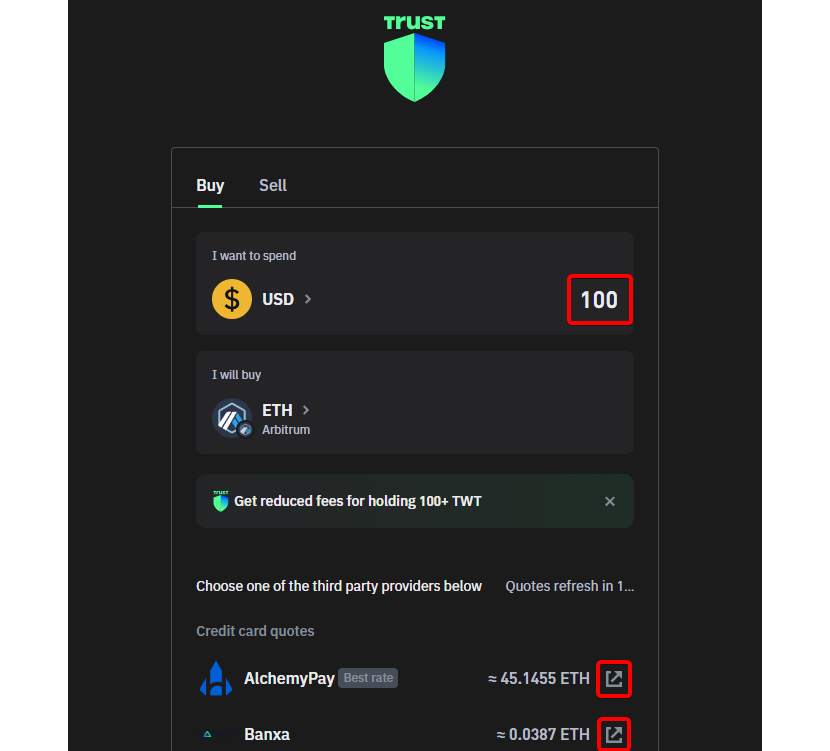
- Step 4: Purchasing ETH: Select a suitable third-party provider, follow the prompts to purchase ETH with fiat currency, and ensure the acquired ETH is specifically on the Arbitrum network.
Option B: Utilizing the "Swap" Feature on Trust Wallet
- Step 1: Accessing the "Swap" Feature: Open the Trust Wallet and locate the "Swap" feature within the app.
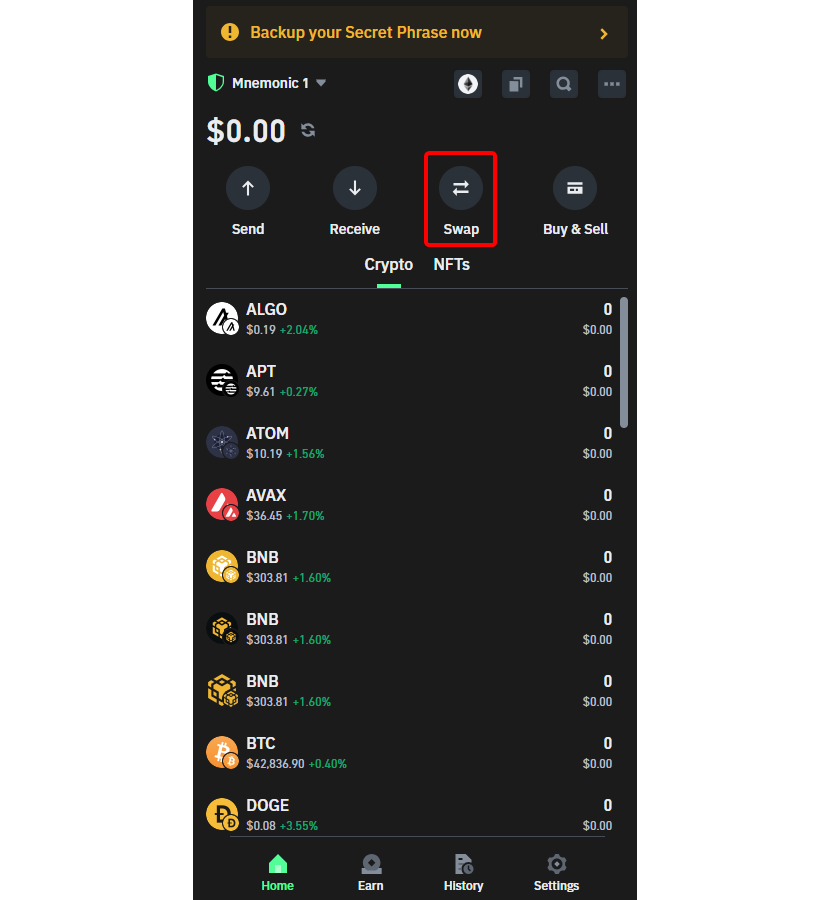
- Step 2: Choosing Cryptocurrencies for Swap: Select Arbitrum (ARB) or any other cryptocurrency you possess within Trust Wallet and wish to convert into Ethereum (ETH) on the Arbitrum network.

- Step 3: Select ETH coin on Arbitrum One and Execute the Swap: Follow the prompts to execute the swap, ensuring that the converted amount reflects ETH on the Arbitrum One network.
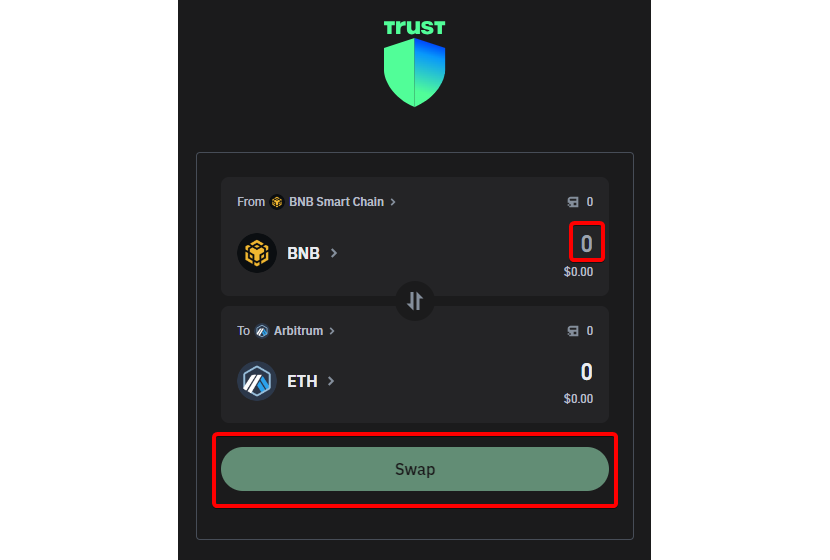
By following these step-by-step guides tailored to each solution, users can confidently navigate the platform and choose the method that aligns with their preferences and requirements. In the subsequent chapters, we will explore an alternative solution outside Trust Wallet, specifically through PlasBit's exchange, providing users with additional options for resolving Arbitrum withdrawal challenges.
Option C: Exploring External Exchange Solutions
While Trust Wallet provides robust internal features for Arbitrum (ARB) withdrawals, some users may prefer exploring external exchange platforms. We will delve into leveraging third-party exchanges and wallets that allow transfers to bank accounts, focusing on understanding the intricacies and nuances involved in this alternative solution.
- Step 1 - Research and Selection: Conduct thorough research to identify reputable external exchange platforms that support Ethereum (ETH) transfers on the Arbitrum One network. Consider factors such as exchange reputation, security features, and user reviews. We will use our platform in this guide.
- Step 2 - Wallet Setup and Verification: Create a wallet on the PlasBit exchange platform, completing the necessary verification steps.
- Step 3 - Funding Your Exchange Account: Deposit crypto into your newly created exchange account.
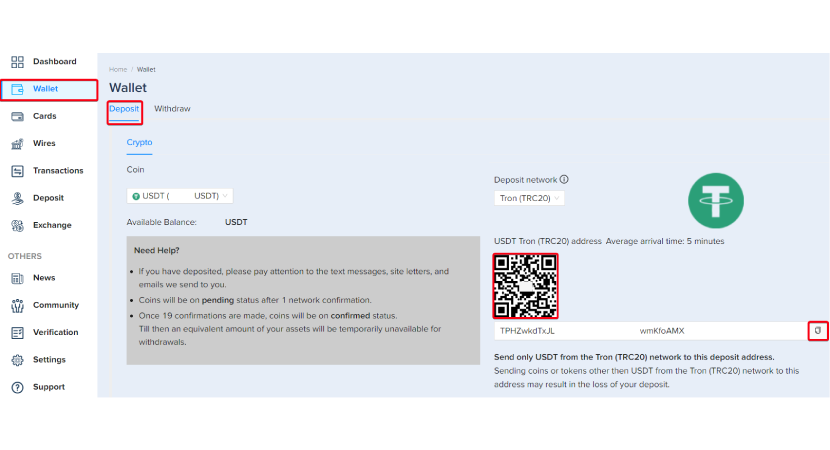
- Step 4 - Go into the Exchange Section: Navigate to the Exchange section to start executing an exchange order.
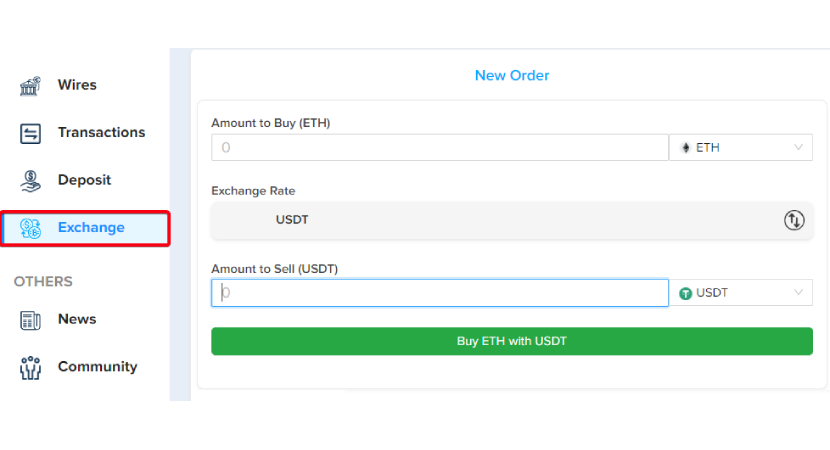
- Step 5 - Exchange into ETH: In the Exchange section, to convert, select the amount of cryptocurrency you wish to sell and select the cryptocurrency you wish to receive.
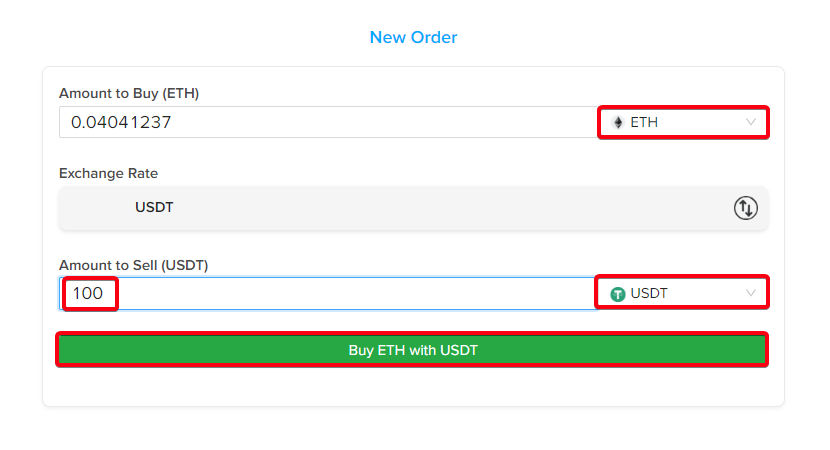
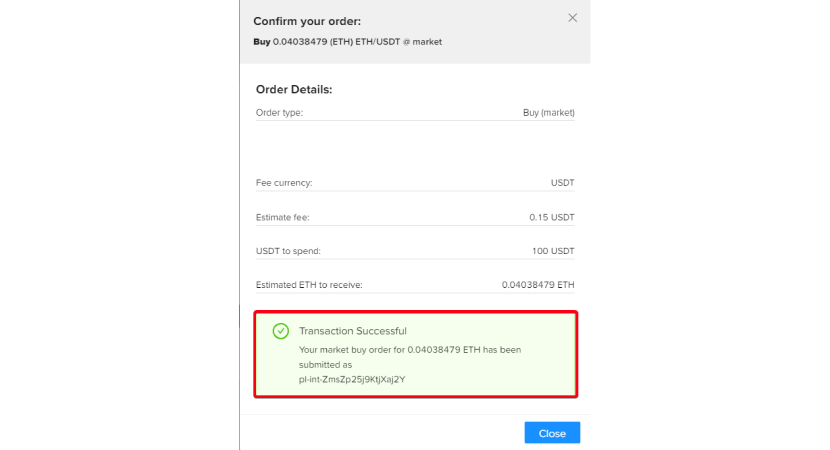
- Step 6 - Confirm the exchange and Get ETH: Once you have correctly verified the conversion data by checking the various parameters, conclude the transaction to receive your ETH.
- Step 7 - Withdrawal Process: Initiate a withdrawal from the external exchange, specifying your Trust Wallet ETH address on the Arbitrum One network.
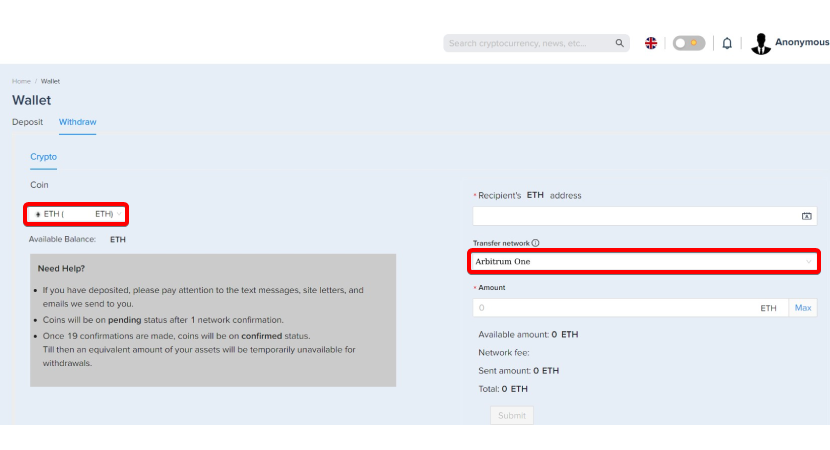
- Step 8 - Confirming Transaction Details: Double-check transaction details, including the recipient's address and network, to ensure accuracy.
- Step 9 - Completing the Transfer: Confirm and complete the withdrawal process, allowing time for the ETH transfer to reflect in your Trust Wallet.
- Step 10 - Accessing Trust Wallet: Open Trust Wallet and access the withdrawal section.
- Step 11 - Completing the Withdrawal Process: Initiate the Arbitrum withdrawal process within the Trust Wallet, leveraging the now-available ETH from the external exchange.
Following these steps, users can effectively utilize external exchange platforms to acquire Ethereum (ETH) on the Arbitrum One network and seamlessly initiate Arbitrum withdrawals on Trust Wallet.
Also, consider that using other exchanges might simplify the procedure, and you would not need Ethereum on the Arbitrum One network to withdraw, as in the image below. This alternative solution provides additional flexibility, catering to diverse preferences and needs in resolving withdrawal challenges.
Unraveling the Smart Contract and Network Compatibility
It's essential to explore the underlying mechanics of smart contracts and network compatibility to comprehend the intricacies of the Arbitrum (ARB) withdrawal issue on Trust Wallet. This chapter aims to shed light on how smart contracts operate and the significance of network compatibility, offering insights into the challenges users face during the transfer process.
The Role of Smart Contracts in Trust Wallet Transactions
In the complex blockchain technology ecosystem, smart contracts emerge as the linchpin facilitating seamless and automated transactions within platforms like Trust Wallet. These intelligent, self-executing contracts encode the terms of agreements directly into lines of code, eliminating the need for intermediaries in executing transactions. In the context of Trust Wallet, the significance of smart contracts becomes particularly pronounced as they play a pivotal role in expediting the transfer of assets, including the native tokens Arbitrum (ARB) and Ethereum (ETH). However, as the efficiency of smart contracts is celebrated, a distinctive challenge arises in the form of an address compatibility dilemma. Both ARB and ETH share the same address format on the Arbitrum network. While efficient for certain operations, this shared format introduces complexity when smart contracts distinguish between assets possessing identical address structures.
Smart Contract Interplay in Withdrawals
The persistence of a shared address format for both ETH and ARB on the Arbitrum network introduces a unique challenge in the interplay of smart contracts during withdrawal attempts. Smart contracts that recognize addresses may encounter difficulties distinguishing between these assets due to their identical address formats. To address this same address dilemma, users must prioritize developing clarity in address recognition for smart contracts. Navigating the complexities of smart contract functionality becomes imperative to ensure accurate and efficient transfers of assets. Users are tasked with unraveling the intricacies of this smart contract interplay to guarantee a smooth and reliable withdrawal process within Trust Wallet.
As we transition to the subsequent chapter, exploring Layer 1 and Layer 2 will further illuminate the complexities influencing Arbitrum withdrawals. This deeper dive will provide users with a comprehensive perspective, empowering them to navigate the nuanced layers of blockchain technology with confidence and understanding.
Layer 1 vs Layer 2: What are the Differences?
In the intricate web of blockchain technology, the concepts of Layer 1 and 2 form the backbone of scalability and efficiency enhancements. A nuanced understanding of these layers unveils the complexities involved and equips users with the insights to navigate the intricacies seamlessly.
Unraveling Layer 1: The Foundation of Blockchain Dynamics
Layer 1 blockchain is the fundamental cornerstone, providing the bedrock upon which decentralized ecosystems are constructed. At its essence, Layer 1 represents the primary blockchain layer, exemplified by prominent platforms like Ethereum.
The Essence of Layer 1
Layer 1, exemplified by Ethereum, is the foundational infrastructure for decentralized transactions. It embodies the principles of security, decentralization, and transparency, establishing a trustless environment where peer-to-peer transactions can transpire without intermediaries. As a quintessential Layer 1 blockchain, Ethereum has been pivotal in pioneering smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps), catalyzing the transformative potential of blockchain technology.
Scalability Challenges in Layer 1
While Layer 1 provides unparalleled security and decentralization, it has inherent scalability challenges. As the blockchain network grows and user activity intensifies, limitations in transaction throughput become apparent. The resulting congestion can lead to slower transaction processing times and increased transaction fees, highlighting the need for innovative solutions to enhance scalability.
Empowering Users through Layer 1 Knowledge
Understanding Layer 1 empowers users to navigate the intricacies of decentralized transactions with clarity. It fosters an appreciation for the foundational principles of security and decentralization while contextualizing the challenges posed by scalability. As users embark on their journey through blockchain dynamics, this comprehension becomes a beacon guiding them through the complex yet transformative world of Layer 1.
Ascending Layers: The Intricacies of Layer 2 Solutions
As our exploration into the blockchain landscape continues, we will focus on the pivotal role of Layer 2 solutions in addressing the scalability challenges posed by Layer 1. Layer 2 represents an innovative approach designed to enhance transaction efficiency and scalability while building upon the solid foundations of Layer 1. In the context of Arbitrum withdrawals on Trust Wallet, understanding the dynamics of Layer 2 becomes paramount.
Layer 2 Solutions Defined
Layer 2 solutions, including prominent examples like Arbitrum and Matic, emerge as a strategic response to the scalability limitations encountered in Layer 1. These solutions are designed to operate on top of existing blockchains, introducing innovations to significantly enhance transaction throughput and efficiency.
Arbitrum as a Layer 2 Scaling Solution
Arbitrum is a noteworthy Layer 2 scaling solution specifically tailored for Ethereum. By leveraging Arbitrum, users can experience heightened scalability without compromising the security and decentralization principles inherent in Layer 1. Arbitrum achieves this by processing a bulk of transactions off-chain, settling them on the Ethereum blockchain.
The Transaction Flow Between Layers
In the context of Arbitrum withdrawals on Trust Wallet, the transactional flow between Layers 1 and 2 is critical. Ethereum (ETH) on the Arbitrum network becomes the bridge, serving as the transactional fuel for operations conducted on Layer 2. This seamless interaction allows users to experience faster transaction confirmation times and reduced fees.
Efficiency and Smart Contracts on Layer 2
Layer 2 solutions introduce a layer of efficiency into the execution of smart contracts. This is particularly relevant when dealing with assets like Arbitrum (ARB) that share address formats with Ethereum. The efficient execution of smart contracts on Layer 2 contributes to a smoother and more accurate withdrawal process for users.
Empowering Transactions Through Layer 2 Knowledge
Comprehending the dynamics of Layer 2 empowers users to navigate the complexities of Arbitrum withdrawals with a heightened understanding. Users can appreciate how Layer 2 solutions optimize transaction flow, providing a more seamless and efficient experience.
Our final chapter will encapsulate the diverse solutions explored throughout this guide, offering users a comprehensive overview and a roadmap to confidently address Arbitrum withdrawal challenges. With knowledge of both Layer 1 and Layer 2, users can embark on their blockchain journeys with enhanced clarity and assurance.
Navigating Arbitrum Withdrawals with Trust Wallet
As our journey through the intricacies of Arbitrum withdrawals on Trust Wallet nears its conclusion, this final chapter serves as a comprehensive overview, consolidating the insights garnered throughout the guide. We've navigated the foundational principles of Layer 1, delved into the innovations of Layer 2, and explored various solutions within Trust Wallet to address withdrawal challenges. Let's distill this knowledge into conclusive guidance for users.
Recapitulating Critical Preparations
At the outset, we emphasized the importance of critical preparations. Activating the Ethereum (ETH) wallet on the Arbitrum network within Trust Wallet, ensuring wallet compatibility, and recognizing the significance of wallet support for the Arbitrum currency laid the groundwork for successful withdrawals.
Step-by-Step Solutions Within Trust Wallet
We provided a meticulous, step-by-step guide for users to navigate the three solutions within Trust Wallet:
- Option A - Purchasing ETH on Arbitrum One: Users can buy ETH directly from third-party companies within Trust Wallet, streamlining the process of covering network fees.
- Option B - Utilizing the "Swap" Feature: Trust Wallet's internal exchange functionality allows users to convert other cryptocurrencies, including Arbitrum, into ETH on the Arbitrum One network.
- Option C - Exploring Third-Party Exchange Platforms: While external exchanges were explored, users can now leverage these platforms to purchase ETH, transfer it to Trust Wallet, and initiate Arbitrum withdrawals.
Understanding Smart Contracts and Network Compatibility
Delving into the intricacies of smart contracts, we deciphered the challenges posed by shared address formats and the importance of network compatibility. Users gained insights into the crucial role played by ETH on the Arbitrum One network in facilitating seamless transactions.
Navigating Layers: Layer 1 and Layer 2 Dynamics
Understanding the dynamics of Layer 2 and Layer 1 was pivotal. As the foundational blockchain, Layer 1 encountered scalability challenges addressed by Layer 2 solutions, such as Arbitrum. The transactional flow between these layers, efficiency in smart contract execution, and the utilization of ETH on the Arbitrum One network became focal points in users' journeys.
A Roadmap for Success
As users embark on their Arbitrum withdrawal journeys, this guide serves as a roadmap, offering a holistic perspective on the challenges and solutions within the Trust Wallet ecosystem. With this knowledge, users can confidently traverse the layers of blockchain technology, ensuring successful Arbitrum withdrawals and a seamless overall experience. In conclusion, if you can’t withdraw Arbitrum from Trust wallet, consider that the convergence of critical preparations, step-by-step solutions, smart contract insights, and a nuanced understanding of blockchain layers positions users for success in their interactions with Arbitrum. May your blockchain endeavors be marked by clarity, empowerment, and the transformative potential of decentralized finance.







