When attempting to transfer tokens on the Cardano blockchain, you may encounter the error you don't have enough ADA to cover network fees, which happens because every transaction on the Cardano network requires ADA, Cardano's native currency, to pay for transaction fees (gas fees) and your wallet doesn’t have enough of it to cover the fee. To resolve this error, use an exchange service to deposit another cryptocurrency into your wallet, exchange it for ADA, and send it to the wallet that lacks the ADA.
This PlasBit article will provide a step-by-step guide to buying ADA on our platform to handle your transaction fees. We’ll also delve deeper into the technical aspects that include transaction fees on the Cardano blockchain and learn about other features of the Cardano platform. Last but not least, we will know how and where you can be a part of the friendly Cardano community so that you can stay updated with current happenings and be in touch with like-minded crypto enthusiasts who use Cardano.
How to Deposit Bitcoin and Exchange It for Cardano on PlasBit
Below is a detailed step-by-step guide on crypto-to-crypto exchange. We will explain how to deposit and exchange Bitcoin for Cardano to address the issue of you don't have enough ADA to cover network fees.
Step 1: Go to the Deposit Section
First, access the deposit section in your PlasBit account to start the process.
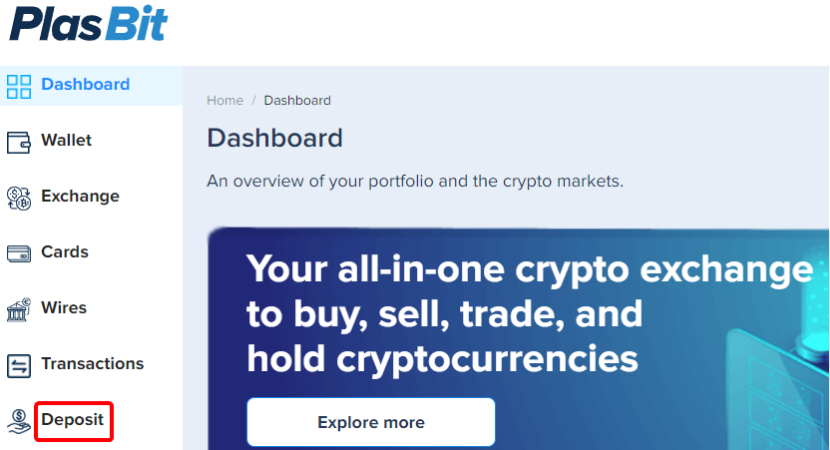
Step 2: Enter Deposit Amount
Enter the amount in fiat that you wish to purchase Bitcoin in.
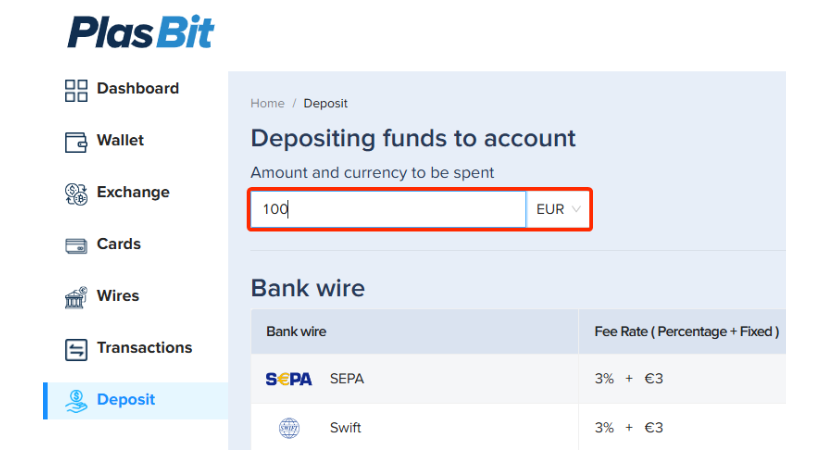
Step 3: Select Bitcoin for Deposit
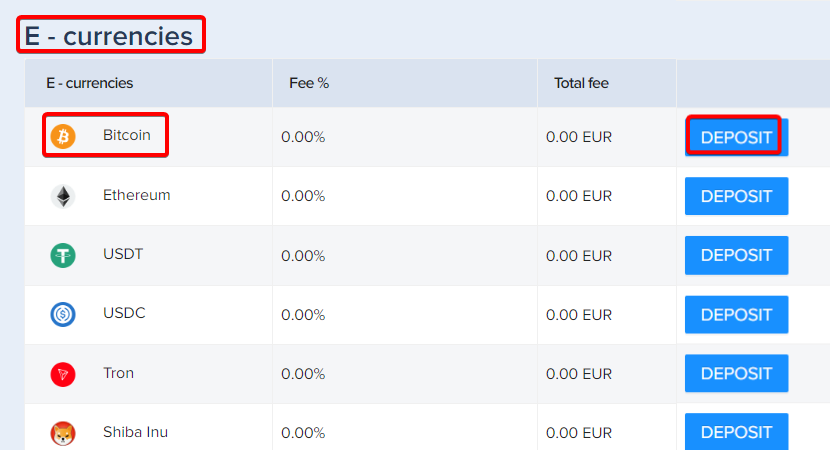
Within the bank wire section, find Bitcoin listed under E-currencies and click on "Deposit" next to it.
Step 4: Transfer Bitcoin
Copy the provided Bitcoin address or scan the QR code to transfer the specified amount of Bitcoin to your PlasBit wallet.
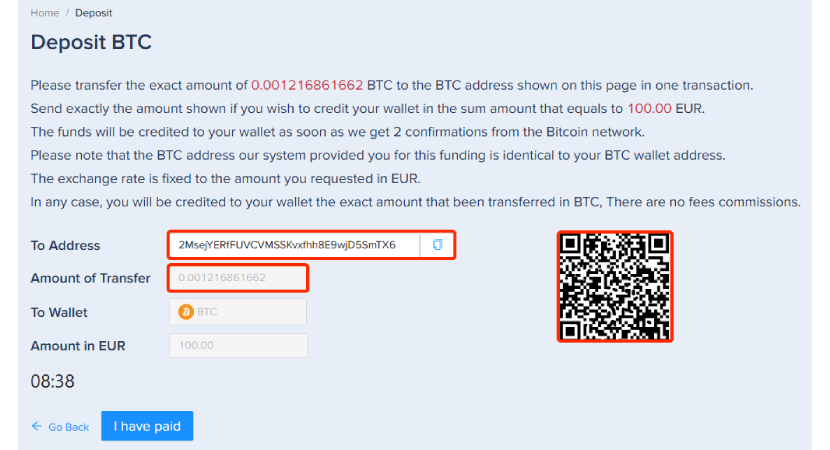
- Note: This transfer requires two confirmations from the Bitcoin network, after which the funds will be credited to your wallet.
Step 5: Verify Deposit and Access Exchange
Once you receive an email confirmation that your BTC is deposited, go to the "Exchange" section.
Step 6: Select ADA
Select ADA from the drop-down menu.
Step 7: Select BTC and Specify the Amount Sell
Select Bitcoin from the drop-down menu and specify how much you want to sell by entering it in the "Amount to Sell" field.
Step 8: Execute ADA Purchase
Click on "Buy ADA with BTC" to finalize the exchange.
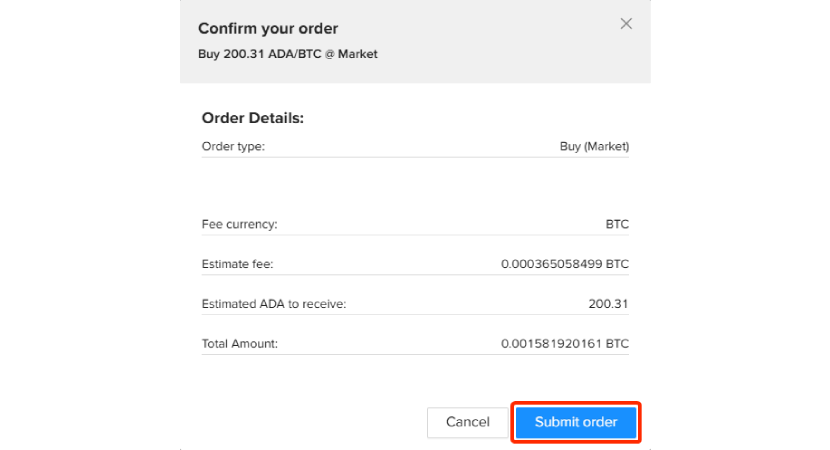
Step 9: Review and Confirm Order
Revise and confirm your order details by clicking on "Submit order."
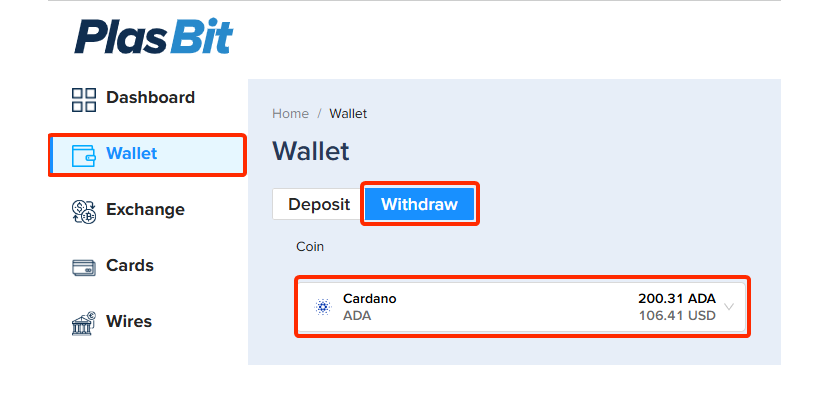
Step 10: Withdraw ADA
After ADA appears in your wallet, go to your wallet section and click on "Withdraw".
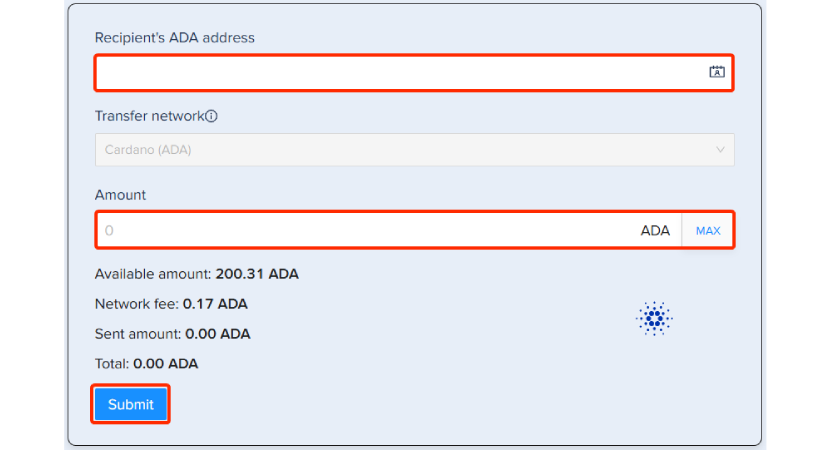
Step 11: Transfer ADA to Stuck Wallet
You can now transfer the ADA to another wallet where coins are stuck due to insufficient network fees.
Following this comprehensive guide ensures that you can manage and resolve fee issues effectively when you don't have enough ADA to cover network fees, enabling the smooth execution of your transactions on the Cardano blockchain
Understanding Layer 1 and Layer 2 Blockchain Technologies
As the core components of the blockchain ecosystem, Layer 1 (L1) and Layer 2 (L2) blockchains each serve distinct roles in how transactions are processed and validated across the network.
Layer 1 Blockchains
First-layer blockchains, or the base layer, are the foundational blockchain networks of Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others. They are mainly involved with sustaining the basic processes, such as checking the transactions, consensus, and security aspects of the network. L1 blockchains’ primary aims include offering more robust security through numerous approaches. Layer 1 blockchains use consensus mechanism to enhance security. Proof-of-work (PoW), used by Bitcoin, requires solving complex puzzles that deter attacks by being computationally expensive. Proof-of-stake (PoS), used by Cardano, has validators stake their crypto to verify transactions, risking their stake if they act dishonestly. Both methods help maintain network integrity and protect against security breaches. However, Layer 1 solutions usually struggle with the issues of scalability, long processing time, and high fees.
Layer 2 Blockchains
Layer 2 solutions are situated above the Layer 1 blockchain to improve scalability and transaction Speed while not reducing the functionality of the Layer 1 blockchain. Some of them are Lightning Network for Bitcoin and rollups for Ethereum. Layer 2 solutions simply transfer operations to other layers, thus freeing Ethereum's primary layer to handle higher traffic with lower fee payments. Nevertheless, they depend on the security and consensus mechanisms of the Layer 1 blockchain and can have additional layers of complexity in their utilization.
Key Differences
Security
Layer 1 is secure due to decentralized consensus mechanisms, while Layer 2 solutions, although still secure, are partially built based on Layer 1’s security frameworks.
Scalability
Layer 1 blockchains like Bitcoin face scalability challenges due to block size limitations, which restrict the number of transactions each block can handle. Smaller block sizes can lead to network congestion, slowing down transaction processing and increasing fees during periods of high demand. Whereas, Layer 2s are built to respond to scalability challenges by handling transactions outside the blockchain.
Complexity
Introducing Layer 2 solutions adds complexity because these solutions need to work smoothly with existing Layer 1 blockchains without altering their fundamental algorithms. While Layer 1 blockchains are responsible for ensuring security and decentralization, Layer 2 solutions are designed to improve scalability and transaction speed. However, to be effective, Layer 2 must integrate with Layer 1 in a way that maintains the integrity of the underlying system, without requiring major changes to how the Layer 1 blockchain operates. This makes the development and implementation of Layer 2 solutions technically challenging.
Investment Safety
Regarding investment safety, it can be stated that Layer 1 blockchains can be considered safer and more reliable because of their recognition and widespread validation. However, Layer 2 solutions are also attractive in the context of higher transaction volumes and lower fees, which may be very useful in rapid-growth industries such as DeFi (Decentralized Finance). In general, the investors should analyze the solutions in layers 1 and 2 and decide which investment should meet the needs of a particular project and the investor's risk tolerance.
Understanding Cardano: A Blockchain Platform for Innovators
Cardano is a third-generation blockchain with unique features, like being developed through evidence-based methods founded on peer-reviewed research. Cardano was started by Charles Hoskinson, a co-founder of Ethereum, with the goal of offering more features than any other protocol ever created. This is because it is the first-ever blockchain platform created based on research as the cornerstone of its development.
Proof-of-Stake Protocol - Ouroboros
Unlike traditional blockchains that rely on proof of work, Cardano uses the Ouroboros proof of stake –a more efficient solution to creating consensus, lowering energy consumption, and maximizing the number of transactions.
Layered Architecture
Cardano uses a two-layer architecture. The transaction layer is known as the Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL), and the computation layer, handling smart contracts and applications, is known as the Cardano Computation Layer (CCL). This separation ultimately provides additional versatility as well as more straightforward maintenance and upgrades.
Decentralized Applications and Smart Contracts
In an update called Alonzo, Cardano added support for smart contracts, which let developers create decentralized applications (dApps) on its platform, expanding its capabilities beyond simple transactions.
Staking
Cardano offers ADA holders a way of contributing to the network through staking, giving the participants a chance to earn from the consensus mechanism.
Sustainable and Secure
Cardano emphasizes safety and scalability and thinks about the full decentralization of its network so that it can be managed solely by its community.
Development and Governance
The development of Cardano can also be described as innovative since Cardano’s project is based on academic research, which is peer-reviewed and publicly available. IOHK (Input Output Hong Kong), the Cardano Foundation, and EMURGO form a team to create the platform. These entities are instrumental in the marketing, advancement, and market embrace of Cardano technology.
Cardano Roadmap
Cardano's development roadmap is organized into five distinct eras, each focusing on a specific aspect of the blockchain's evolution:
Byron (Foundation)
This first stage laid down the structural design of Cardano and allowed individuals to engage in purchasing and selling ADA, the native token within the network. It introduced the Ouroboros consensus protocol and the Daedalus wallet, setting the stage for future developments.
Shelley (Decentralization)
Building upon Byron, the Shelley era endeavored to change Cardano from a federated network to a decentralized one. This was achieved by encouraging community-run nodes and implementing a delegation and incentives scheme to promote stake pools, enhancing the network's security and robustness.
Goguen (Smart Contracts)
The Goguen phase brought smart contract capabilities to the Cardano platform so developers could create dApps for it. This era also brought about the multi-currency ledger, enabling the creation of native tokens and broadening the network's utility.
Basho (Scalability)
Emphasizing the improvement of optimization, the Basho stage is directed at expanding Cardano’s capabilities. Key developments include the introduction of sidechains and performance improvements to support high transaction volumes and diverse use cases.
Voltaire (Governance)
The last level is to reshape the governance system in a self-organizing way. It introduces voting mechanisms and a treasury system, empowering the community to influence the network's future development and ensure long-term sustainability.
Each of them is a major step in the evolution of the Cardano project towards a decentralized blockchain platform with open-sourced scalability.
Applications and Collaborations
Cardano has been used in different industries, such as education, retail, agricultural, governmental, financial, and health industries. Notably, it has aligned itself with the Ethiopian Ministry of Education to produce a blockchain for credentialing students. These use case examples show how Cardano can be applied to positively influence and improve society and people’s lives.
Investment Perspective
Cardano has a proof of stake model that is generally less expensive than proof of work chains like Bitcoin. While Cardano is a fairly recent project, the perpetual development and expansions of features set within its ecosystem make it a unique investment opportunity.
Final Thought
Cardano is not only a cryptocurrency but an ambitious platform for the blockchain of the future’s technological and government responsibilities with the intention to have a positive impact on the world. Because of its state-of-the-art design, evident scientific approach, and comprehensive strategic plan, Cardano can be considered a versatile solution for many industries and different fields. While growing more decentralized and expanding its reach, Cardano remains among the interesting projects in the world of cryptocurrencies.

Understanding Transaction Fees on the Cardano Blockchain
The Cardano blockchain uses transaction fees, and this section explains every aspect of it.
Calculation of Transaction Fees
On the Cardano blockchain, transaction fees are determined using a simple formula: a * size(tx) + b. Here, “a” and “b” are protocol constants: “a”, depending on the size of the transaction in bytes, and “b”, the minimum fixed fee, strengthening the network against spam or DDoS threats. This Formula makes the cost go up with the size of the transaction and is a good representation of how many resources it takes to process and store this transaction.
Fixed and Predictable Fees
In contrast to other projects, where the fee may vary depending on network traffic, Cardano has its primary goal to maintain the fee constantand predictable. This approach does not only help to further reduce the fee structure but also assists in increasing user satisfaction by delivering constant and affordable fee rates.
Determinism in Transaction Costs
Cardano emphasizes high assurance and security, and this is demonstrated by its deterministic approach used when handling transactions. This means that the cost and effects of the transactions specified by the users can be easily anticipated in advance, giving users the ability to know the exact impact that their actions will have within the ledger without any uncertainty caused by the volatility of the transaction fees.
Why Transaction Fees are Necessary
There are many reasons behind the transaction fees on the Cardano blockchain, including their importance for the long-term sustainability of the network. The costs of processing transactions and storing data must be accounted for, ensuring that validators are fairly compensated for their computational efforts. In addition, users must pay fees to avoid overloading the network with small or fraudulent transactions, which could disrupt its performance.
The transaction fee system on Cardano serves several key purposes. It compensates validators for their participation in maintaining the blockchain's integrity, helps protect against spam attacks by making it costly for spammers to flood the network, and controls the allocation of resources, thereby enhancing the efficiency and scalability of the blockchain. The fee structure on Cardano is designed to balance reasonable costs while maintaining both security and relatively swift transactions.
Popular Cryptocurrencies Built on the Cardano Blockchain
The Cardano blockchain hosts a variety of decentralized applications (dApps) and cryptocurrencies, reflecting its growing ecosystem. Here's a list of some of the most notable cryptocurrencies built on Cardano:
Minswap (MIN)
Minswap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) built on Cardano with multi-pool options to support different Cardano-based assets. It offers platform tools for newcomers and experts, such as liquidity pools, yield farming, and staking services. Organized with a minimal cost and trading interface, Minswap is used to swap tokens and amplify Decentralized Finance (DeFi) interactions on the Cardano platform.
SundaeSwap (SUNDAE)
SundaeSwap is another decentralized exchange built on the Cardano platform, and it is an automated market maker (AMM) kind of exchange. It enables users to exchange, stake, and farm tokens with trusted security. Owned and operated by its native token, SUNDAE, SundaeSwap allows its token holders to decide on its upgrades, shaping the protocol's future direction.
MELD (MELD)
MELD is a good example of a decentralized, non-custodial banking protocol on the Cardano blockchain, supporting services such as crypto and fiat lending and borrowing. The platform will help reduce the overall complexity of financial interactions and the bureaucracy often associated with formal banking as it is not hindered by many of the organizational and administrative challenges.
CNFT
CNFT is an ecosystem that deals with the Cardano native NFTs, through the platform for users to mint, trade and sell NFTs. It was one of the first marketplaces of NFT on the Cardano blockchain, offering creators and collectors to interact with digital assets in many forms, ranging from art to gaming items.
World Mobile Token (WMTX)
The World Mobile Token is a digital asset in the World Mobile Chain project that targets to increase the availability of mobile network services through a blockchain format. To run network operations, token staking, and rewards within this ecosystem, WMTX is utilized across the ecosystem.
COTI
COTI is a decentralized fintech on Cardano and an open platform where organizations and users can build their own payment systems and digitize any money. It fosters innovation in the payment systems and collaboration with conventional financial systems.
Wingriders (WRT)
Wingriders is a top DEX assisting the Cardano blockchain project and includes token exchange, staking, as well as yield farming. It supports a large number of liquidity pools and is expected to improve decentralized finance (DeFi) activities through offering a secure trading environment.
SpaceBudz (SBZ)
SpaceBudz is an NFT project on Cardano based on animated characters designed to fit the space traveling adventure. It will enable bidding and trading of NFTs on the platform to improve digital collection on the Cardano network.
These cryptocurrencies and tokens illustrate the wide range of financial, creative, and technological endeavors being implemented on the Cardano platform, as well as the increasing adoption of them. If you are looking to invest in these tokens and you're managing ADA to cover network fees and encounter the error you don't have enough ADA to cover network fees, at PlasBit, we have provided the easiest solution to buy ADA and transfer it to your wallet easily.
Success Story: David Lee's Investment in Cardano
David Lee, a mid-twenty IT consultant, entered into the crypto world in late 2019 by investing in Cardano (ADA). When the company was launched, David, who was an engineering student at the time, was attracted to Cardano due to its focus on academic research and new technologies, given that the company had little to no capital to begin with. Fascinated by Cardano’s stated proof-of-stake consensus method, which offers better scalability and efficiency than the proof-of-work approach, David carefully studied the project, having a vision for its future growth.
For the years, as Cardano introduced core upgrades such as the Vasil update, largely boosting the network's performance and flexibility of smart contracts, David’s initial investment grew considerably. The Vasil upgrade, named after a late mathematician and Cardano fan, changed things because it helped increase block creation speed and lower the price of decentralized applications, making David confident in his investment decision.
However, David’s success story is even more phenomenal, given that the crypto market is well known for its high risks. Nonetheless, his strategic thinking and constant effort to learn about blockchain technology finally yielded the result, significantly increasing his initial capital. This example is a good illustration of the need for research and patience when investing in cryptocurrencies. David’s case shows that putting your money into a technology you trust, similar to Cardano's Layer 2 scaling solutions, supported by a strong community and continuous development, would bring substantial rewards.
In light of these findings, David’s experience should provide useful insights for investors planning to engage in similar projects to undertake thorough research into the technological foundation and communities, as well as stay informed about market trends and developments.
Understanding the Active Community Behind Cardano
The Cardano Forum is an active and growing community that participates in different discussion forums on various aspects of the Cardano project. These forums are essential for working, regulating, and teaching about blockchain’s advancement and usage. Discussions on these issues occur on the Cardano Forum, which contains sections in various languages and topics ensuring worldwide accessibility.
Major Threads of Conversation in Cardano Forums
Development
This section is designed to host technology topics covering details of Cardano's codebase, where developers offer and discuss project updates.
Governance
The participants engaged in the discussion and decided to develop Cardano’s protocol further, emphasizing the network's decentralized system of governance and policy-making.
Technical Support
A weblog that pays particular attention to technical issues that users will likely encounter when using the internet to make transactions or deal with wallet issues. For example, if a user receives a message like ‘You don’t have enough ADA to cover the network fee, they can receive some assistance and recommendations in this forum.
Education and Resources
This part offers educational materials and tutorials for new and seasoned users to enhance their knowledge of blockchain and expand their understanding of ADA and Cardano.
Communication with the Members of the Cardano Community
Anyone wanting to use the Cardano blockchain or create something on top of it may apply for the Cardano Forum user account. Here, users can join discussions to ask for support and contribute to Cardano's progress. Whether you have technical problems such as “you don’t have enough ADA to cover the network fees” or broader topics like decentralized finance applications, this forum is an excellent point of referral to seek information and community support.
Conclusion
A common challenge for Cardano users is facing the error you don't have enough ADA to cover network fees when sending transaction fees every time they attempt. Sometimes, it is not very pleasing, especially when the network is busy and the fees are high. This issue can be annoying, especially when the network is busy and fees are higher. Our exchange provides a straightforward, step-by-step process for depositing Bitcoin and converting it to Cardano so that they always have enough balance of ADA to pay the transaction fees, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted transactions on the Cardano blockchain. The process of depositing Bitcoin into our exchange and then converting it into Cardano was well-outlined in this article.
Furthermore, knowing about various levels of blockchain, for example, Layer 1 and Layer 2, will allow users to select the most suitable blockchain solutions. Anyone facing high transaction fees on Cardano (Layer 1) can switch to Layer 2 protocols for even faster and cheaper transactions. At PlasBit, we assist our users through these challenges, guaranteeing they get the best experience in their Cardano transactions by having enough ADA to move forward.







