As of now, the blockchain Dogecoin network is based on the Proof of Work mechanism and uses a fee based system to verify transactions. The fee or the "gas" of the network is the network native token $DOGE and transaction fees are typically very low compared to other blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum. The fees can range anywhere from 0.01 DOGE to 1 DOGE, depending on the transaction size and are being rewarded to the miners as a payment method for their role in verifying transactions in the blocks they mine. Dogecoin's transaction fees are based on the size of the transaction in bytes, not the value of the transaction of the DOGE being sent. Now that we briefly recapped that DOGE is the fee of the Dogecoin Network and you get an error when you’re trying to transfer DOGE on the Dogecoin network you don't have enough DOGE to cover network fees it happens because, for every transaction on the Dogecoin network, you need to pay gas, which means a transaction fee in order for the transaction to be processed. The fee is paid using the dogecoin native token called DOGE, and there isn’t enough DOGE in your wallet to pay the fee. To fix this issue you can deposit euro or any other crypto to an exchange wallet, exchange it to DOGE, and transfer the DOGE from your exchange wallet to your external wallet. This way, you will be able to pay the transaction fee and transfer the stuck DOGE. This article also discusses Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains before delving into the world of Dogecoin and Meme coins.
How to Increase Your DOGE Balance
We'll show you how to exchange Bitcoin to DOGE and transfer it to another wallet when you don't have enough DOGE to cover network fees.
Step 1 – Access the deposit section
Access the deposit section in your account to start the process.
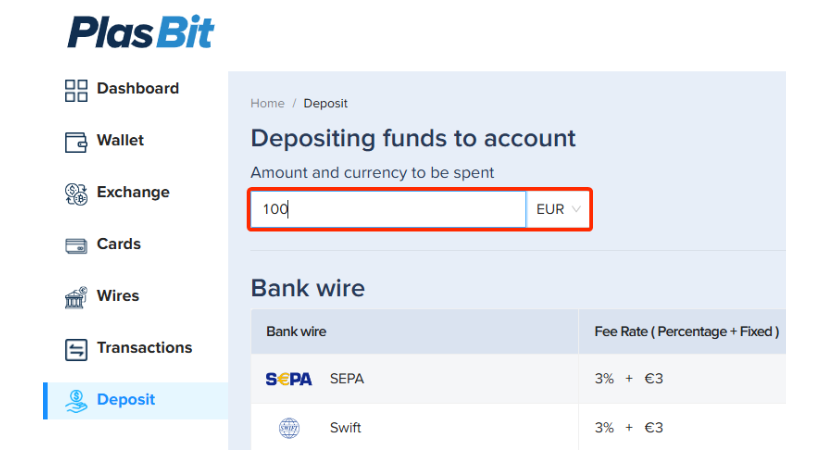
Step 2 – Enter fiat amount
Enter the amount in fiat that you wish to purchase Bitcoin in.
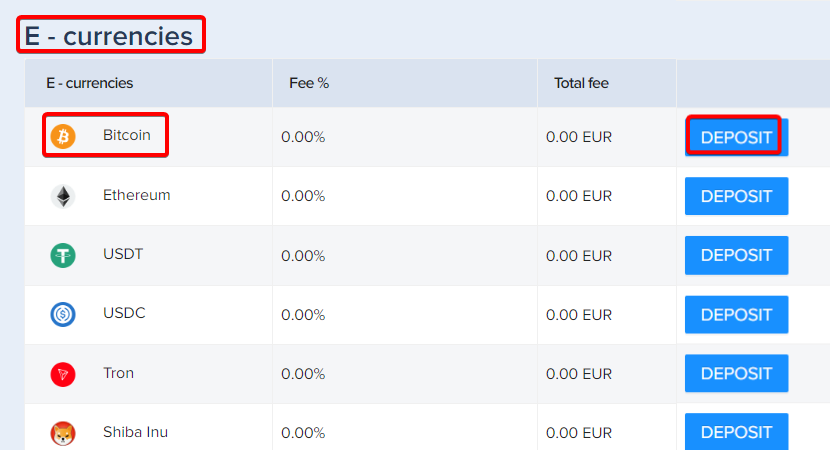
Step 3 – Deposit Bitcoin
Find Bitcoin listed under E-currencies in the bank wire section. Click on "Deposit" next to it.
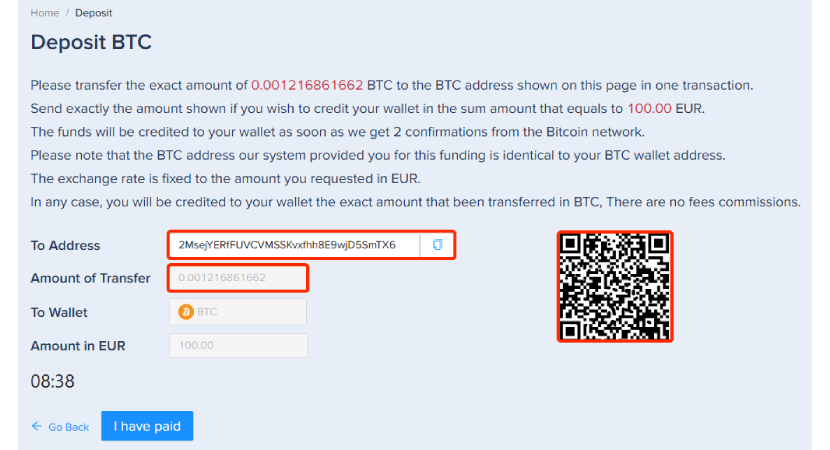
Step 4 – Transfer Bitcoin to your wallet.
Copy the provided Bitcoin address and the specified amount, or scan the QR code to transfer Bitcoin to your PlasBit wallet. This transfer requires two confirmations from the Bitcoin network, after which the funds will be credited to your wallet.
Step 5 – Exchange Section
Once you receive an email confirmation that your BTC is deposited, go to the "Exchange" section.
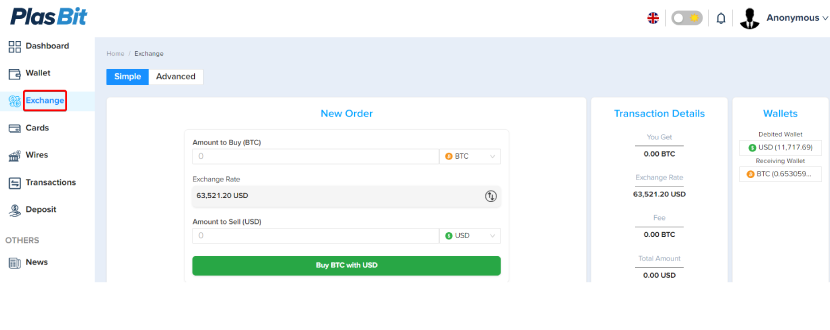
Step 6 – Select DOGE
Select DOGE from the drop-down menu.
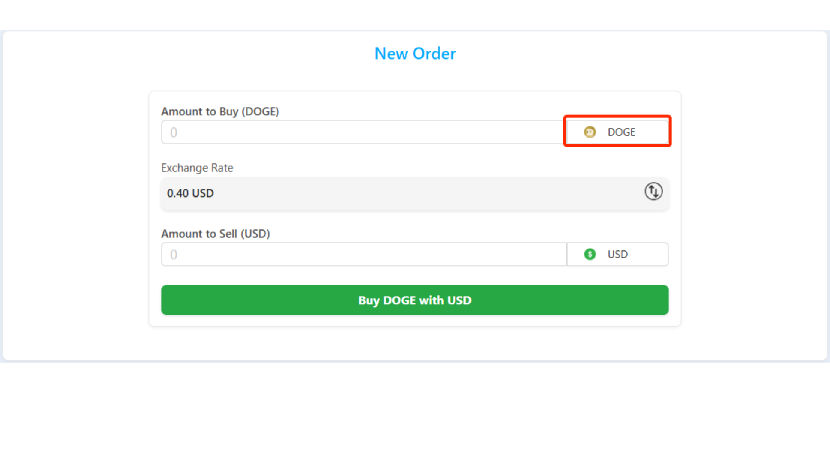
Step 7 – Select Bitcoin
Select Bitcoin from the drop-down menu.
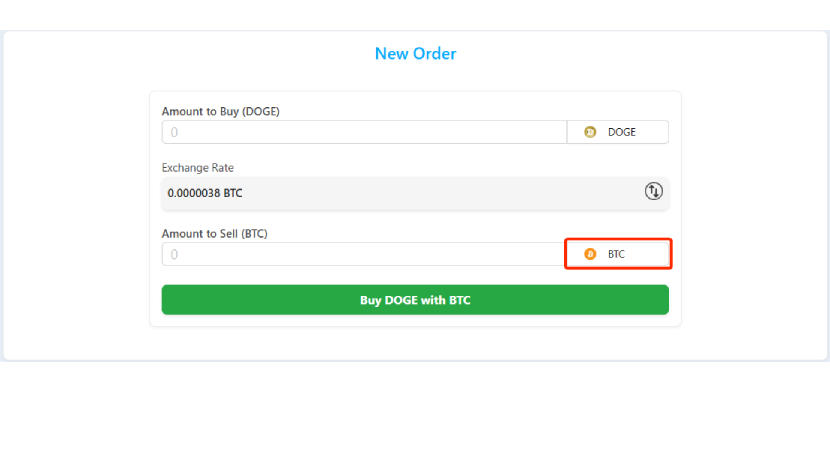
Step 8 – Enter the amount to sell
Specify how much you want to sell by entering it in the "Amount to Sell" field.
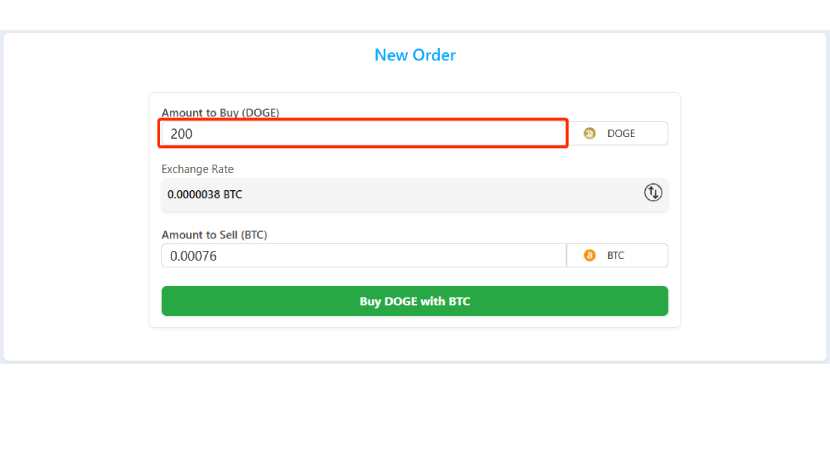
Step 9 – Finalize the exchange
Click on "Buy DOGE with BTC" to finalize the exchange.
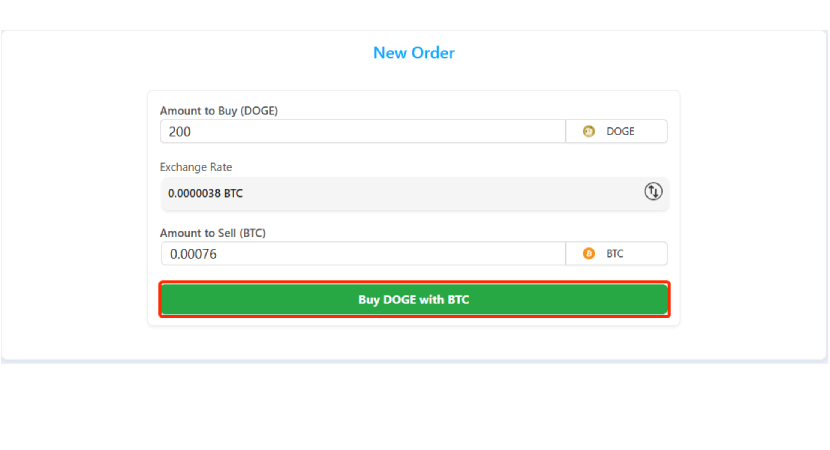
Step 10 - Revise and Submit Order
Revise and confirm your order details by clicking on "Submit order."
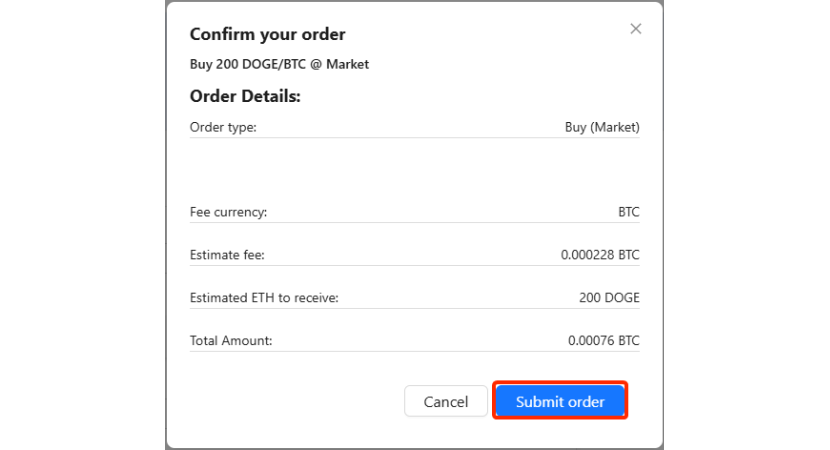
Step 11 – Withdraw DOGE
After DOGE appears in your wallet, go to your wallet section and click on "Withdraw."
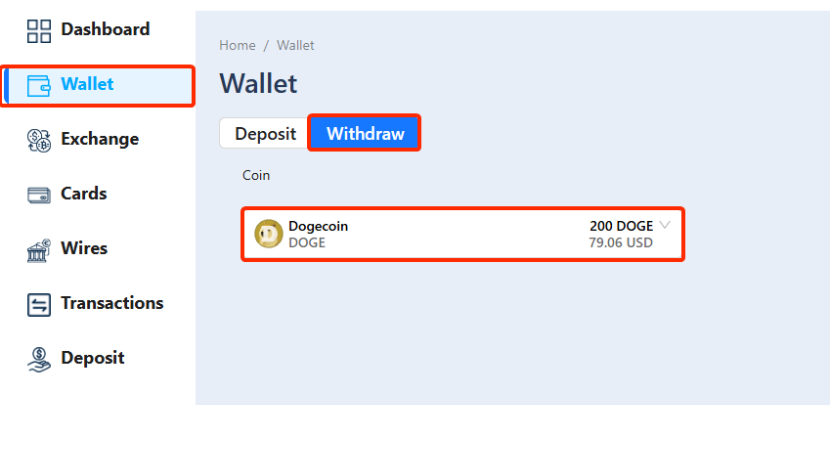
Step 12 – Transfer DOGE to another wallet.
You can now transfer the DOGE to another wallet where coins are stuck because you don't have enough DOGE to cover network fees.
Layer 1 and Layer 2 Blockchain
Layer 1 Blockchains – The Base Layer
Layer 1 (L1) blockchains are the base layer of blockchain networks, providing the infrastructure for secure, decentralized, and transparent transactions. They operate independently, validating and executing transactions directly on their main chain without relying on other blockchains. Control is distributed across numerous nodes, reducing the risk of single points of failure, ensuring a high level of security, and making the blockchain robust and reliable. L1 blockchains can execute smart contracts (self-executing contracts with terms written into lines of code), allowing for automated transactions. They serve as the underlying base for many Layer 2 solutions, which are designed to enhance scalability and speed. They set the stage for decentralized applications (dApps) and other protocols, ensuring the integrity of the network. L1 blockchains usually have their own native cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin for the Bitcoin blockchain or Ether for the Ethereum blockchain, which are used to facilitate transactions and incentivize network participation. Despite their robustness, L1 blockchains often face scalability issues. As the number of users and transactions grows, the processing capacity can become strained, leading to delays and increased fees. The most common scaling techniques are:
· Increased block size – An increased block size allows more transactions to be verified and expands the overall capacity of a network.
· Sharding – Sharding allows a blockchain database to be broken into smaller parts to process transactions simultaneously.
· Reducing Block Time -Decreasing the time it takes to mine a block can increase the overall speed of the blockchain. However, this can lead to more orphan blocks, which are legitimate blocks that must be discarded by the network due to conflicts
· Consensus Mechanism - Choosing or upgrading the consensus algorithm can significantly impact the scalability of a blockchain. For instance, Ethereum's transition from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) aims to achieve more efficient transaction validation and higher throughput. Blockchain architecture is designed with a layered structure, layers that work together to enable the functioning of a blockchain network. They are:
(a) The Hardware Layer - the physical infrastructure used to run nodes in the blockchain network. It is a decentralized network of nodes, and different entities may operate each node.
(b) The Data Layer - ensuring that the information is tamper-proof and all the participants in the network can verify it.
(c) The Network Layer - facilitating communication and connectivity between nodes in the network. Nodes communicate with each other to process transactions, validate them, and share information about the state of the network.
(d) The Consensus Layer - enabling nodes to agree on the state of the blockchain and validate transactions. Common consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT).
(e) The Application Layer - where decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts are built and executed.
Layer 2 (L2) Blockchains – The Secondary Layer
Layer 2 solutions are built on top of L1 blockchains to enhance scalability and transaction speed. Examples include the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and rollups, sidechains, and state channels for Ethereum. They focus on improving the scalability and efficiency of transactions by processing them off-chain or in parallel and then consolidating them into a single transaction on the main chain. This system reduces the load on the main chain and increases transaction speed. L2 solutions can slightly compromise on security compared to L1, and they generally rely on the underlying L1 blockchain for overarching security measures. This balance allows for faster and more cost-effective transactions without fully sacrificing security. Layer 2 protocols are more flexible and can be tailored to specific needs, such as handling high-frequency transactions or reducing transaction costs, without altering the base layer's fundamentals.
Key Differences
· L1 blockchains enhance the base layer through protocol updates, while L2 solutions build upon the existing L1 infrastructure to provide scalability and efficiency improvements.
· L1 blockchains process transactions directly on the main chain, whereas L2 solutions handle transactions off-chain or in parallel before consolidating them on the main chain.
· L1 prioritizes security and decentralization, potentially at the expense of speed and scalability, while L2 prioritizes agility and reduced costs, relying on L1 for security.
Types of Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 2 (L2) blockchain solutions are designed to enhance blockchain networks' scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness without compromising their security or decentralization. Each of these Layer 2 solutions addresses different aspects of scalability, cost, and privacy, making them suitable for various use cases such as payments, DeFi, gaming, and NFT marketplaces.
Optimistic Rollups
Transactions are processed off-chain and then batched together for settlement on the mainchain. Validators use Merkle roots to verify the transactions, and there is a dispute period to challenge any transactions that look fraudulent. This method supports smart contracts similar to the underlying blockchain but has a more extended dispute period than ZK rollups. Optimistic rollups rely on economic incentives and game theory to validate transactions.
ZK Rollups
Zero Knowledge (ZK) rollups use advanced cryptographic proofs (zk-STARKs or zk-SNARKs) to validate transactions off-chain and batch them together for settlement on the main chain. Key benefits include reduced transaction fees, enhanced privacy, faster transaction processing, and efficient use of blockchain capacity.
State Channels
State channels are two-way communication channels that allow participants to interact and transact off-chain. Participants lock funds in a multi-signature smart contract on the main chain, and then they exchange signed messages off-chain, updating the channel's state. When they are ready, they close the channel by submitting the final state to the main chain. This approach reduces transaction fees, enhances privacy, and provides near-instant transaction finality.
Plasma
Plasma is a Layer 2 solution that involves creating child blockchains (Plasma chains) that periodically commit their state to the main blockchain. This structure allows for higher transaction throughput, reduced costs, and improved scalability. However, Plasma chains can be complex to manage and may have limitations in terms of usability.
Side Chains
Side chains are separate blockchains that run in parallel to the main blockchain. They allow assets to be transferred between the main and side chains, enabling increased scalability, reduced transaction costs, and enhanced scalability. Examples include Polygon's various side chains like Polygon PoS and Polygon Miden
Off-Chain Computation
Off-chain computation involves processing certain parts of transactions or smart contract executions outside the main blockchain, reducing the computational load on the main chain. This structure can be seen in solutions like Celer Network, which focuses on blockchain interoperability and off-chain computation.
Bitcoin Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a Layer 2 solution specifically for Bitcoin, using bidirectional payment channels (a type of state channel) to process transactions off-chain. It offers instant payments, scalability, low costs, and cross-blockchain swaps.

Dogecoin
If you don’t have enough DOGE to cover network fees, chances are you know all about Dogecoin, but let’s explore a little of its history. Dogecoin began as a satirical response to the hype surrounding cryptocurrencies at the time of its creation. It launched on December 6, 2013, and, to this day, its website defines it as "the accidental crypto movement that makes people smile!"
Two software engineers created Dogecoin and its community:
· Billy Markus, a software engineer at IBM, was the primary developer behind the initial releases of Dogecoin.
· Jackson Palmer, who worked at Adobe in Sydney, Australia, was the other co-creator. He is credited with creating the Dogecoin.com website and was the public face of Dogecoin in its early days. Palmer's efforts in marketing and promoting the coin significantly contributed to its initial success. By 2014, both founders had left the development efforts, and a Dogecoin Core Development team had been formed to maintain and develop the cryptocurrency further. Over the years, this team has been supported by over 40 contributors. In 2015, Jackson Palmer left the cryptocurrency community entirely, expressing concerns about the exploitative nature of cryptocurrencies. Billy Markus departed around the same period, citing online harassment and death threats as reasons for his exit. Dogecoin was created using the open-source code from Litecoin, which is itself a fork of the Bitcoin blockchain. The cryptocurrency was inspired by the popular "Doge" meme featuring a Shiba Inu dog called Kabosu, with multi-colored comic sans text representing the dog's "thought bubbles". Despite its origins as a joke, Dogecoin quickly gained traction. Within the first two weeks of its launch, it reached more transactions per day than Bitcoin, and by December 19, 2013, its value jumped nearly 300% in just 72 hours, rising from $0.00026 to $0.00095. The Dogecoin community was involved in several charitable endeavors in its early years. For example, in 2014, the community raised funds to send the Jamaican bobsled team to the Sochi Winter Olympics and to build clean-water wells in Kenya.
The community also played a crucial role in Dogecoin’s growth. The currency was widely used on platforms like Reddit as a tipping currency to show appreciation for content or to support charitable causes. This community-driven approach fostered a sense of inclusivity and fun, attracting a large number of users. By the end of its first month, Dogecoin.com had over one million unique visitors. In January 2014, Dogecoin's trading volume briefly surpassed that of all other cryptocurrencies combined, although its market capitalization remained behind that of Bitcoin. The cryptocurrency experienced significant price fluctuations, including a low of $0.0000869 in May 2015 and a peak of $0.017 in January 2018 during the cryptocurrency bubble. Dogecoin's popularity reached new heights in 2021, driven by high-profile endorsements from celebrities such as Elon Musk, Snoop Dogg, and Mark Cuban. The currency's value surged over 800% in 24 hours in January 2021, and it continued to rise throughout the year, reaching a peak market capitalization of over $85 billion in May 2021. This surge was partly fueled by the WallStreetBets subreddit community and a TikTok trend aimed at getting Dogecoin to $1. Overall, its growth from a satirical meme coin to a significant player in the cryptocurrency market is a testament to the power of community engagement and the unpredictable nature of the crypto space. Dogecoin's ability to surpass Bitcoin in transaction speed and volume can be attributed to several key differences in their design and implementation:
· Transaction Speed - Dogecoin has a significantly faster block creation time than Bitcoin. While Bitcoin takes approximately 10 minutes to create a new block, Dogecoin creates a new block every minute. This faster block time allows Dogecoin to process transactions much quicker, with confirmations typically taking around 6 minutes, as opposed to Bitcoin's 60 minutes.
· Transaction Throughput - Dogecoin can handle about 30-40 transactions per second (TPS), substantially higher than Bitcoin's 3-7 TPS. This higher throughput directly results from the faster block creation time and the larger block size relative to Bitcoin.
· Consensus Mechanism and Mining - Although both Bitcoin and Dogecoin use the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, Dogecoin uses the Scrypt algorithm, which is less dependent on Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) compared to Bitcoin's SHA-256 algorithm. This mechanism makes mining more accessible to a broader audience using standard graphics processing units (GPUs). Additionally, Dogecoin's merged mining with Litecoin enhances its computational power and security.
· Block Size and Scalability - Dogecoin's design allows for more transactions to be included in each block due to its faster block creation and potentially larger block size. This scalability advantage enables Dogecoin to handle a higher volume of small transactions efficiently, making it more suitable for tipping and small transactions.
Elon Musk's Impact on DOGE
Musk's endorsements and comments have repeatedly caused substantial fluctuations in Dogecoin's market price. For instance, a single tweet from Musk has led to a 50% increase in Dogecoin's value within hours. A phenomenon known as the "Elon Musk Effect" or the "Dogefather Effect." His tweets can cause the value of Dogecoin to rise or drop rapidly, depending on the nature of his message. This volatility has made Dogecoin a closely watched asset, with investors monitoring Musk's Twitter feed for potential investment signals. Musk's support has brought Dogecoin into mainstream media coverage, highlighting its unexpected price surges and high-profile supporters. His appearance on Saturday Night Live in May 2021, where he joked about Dogecoin, further amplified its cultural significance. Dogecoin has become a symbol of internet culture entering traditional finance, with phrases like "To the moon!" becoming associated with its aspirational price targets. Musk has hinted at integrating Dogecoin payments into his various ventures, such as Twitter (now X) and potentially Tesla.
These speculations have driven interest in the cryptocurrency, demonstrating its potential as a payment method and increasing its perceived value and utility. His positive endorsements, often accompanied by memes and quirky remarks, generated enthusiasm among investors, increased trading activity, and attracted new buyers, resulting in substantial returns for early investors. However, the associated volatility also presents risks, such as sudden drops in value that can result in significant losses for those who bought in at higher prices. Dogecoin has become a cultural phenomenon, with the coin becoming a topic of mainstream conversation. Musk's tweets have fueled the viral nature of Dogecoin, making it a symbol of the power of internet communities to influence real-world markets.
Memecoins
Meme coins (or memecoins) are cryptocurrencies inspired by popular internet phenomena, such as memes, which are creative content that spreads through the internet and social media, often conveying humorous or ironic messages. DOGE, created as a joke, is considered the original memecoin. Meme coins are characterized by their playful and often humorous origins, aiming to attract users through fun and light-heartedness. They create strong, often humorous communities where investors and fans come together to celebrate the coins and associated memes, fostering a sense of belonging and shared identity. Their prices are highly volatile and can be driven by social media trends, pop culture, and mentions by influential personalities.
This volatility can lead to rapid price increases or decreases. Some meme coins are seen as speculative investment opportunities despite their humorous origins. Their popularity can rise quickly, leading to significant but volatile gains. However, they carry considerable risks, such as high volatility and the potential for rapid price drop. Many meme coins do not have any practical use or utility beyond being a token, which can make them less stable compared to other cryptocurrencies. Some countries have taken steps to regulate or ban meme coins because they lack clear objectives or substance. Generally speaking, meme coins are inexpensive and can be purchased at various cryptocurrency exchanges, making them accessible to a wide range of investors. However, it is important to do thorough research, understand the risks, and only invest what they can afford to lose, as meme coins should not be the cornerstone of a cryptocurrency portfolio.
Other examples of Meme coins
Here are some of the most popular meme coins currently available. These meme coins are popular due to their strong community engagement, unique features, and the potential for significant price movements driven by social media and internet trends.
· Bonk (BONK) - Launched on the Solana network, Bonk gained significant attention in 2023, with gains of over 7,300%. It continues to be a top meme coin with the launch of its decentralized exchange, BonkSwap.
· Shiba Inu (SHIB) - Inspired by the Dogecoin community, Shiba Inu has become one of the most popular meme coins. It has seen significant gains, with recent developments like adopting Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) and launching the Shiba Name Service.
· Pepe (PEPE) - It burst onto the scene in 2023 and remains one of the top meme coins in terms of market capitalization. It is known for its lack of utility but significant price growth.
· Myro (MYRO) - Built on the Solana blockchain, Myro aims to increase the accessibility and enjoyment of cryptocurrencies. It has seen gains of over 1,400% in 2023.
· FLOKI - Part of the Floki Inu ecosystem, FLOKI is both a utility token and a meme coin. It follows a deflationary model with auto-burns and has multi-chain functionality on Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain.
· Dogwifhat (WIF) - Built on the Solana blockchain, Dogwifhat gained momentum in 2023 with its humorous branding. It continues to see strong trading activity despite significant price corrections.
· JetBolt (JBOLT) - A young altcoin with a lightning-cat mascot and zero-gas technology, it has sold over 100 million tokens since its presale began.
· Peanut the Squirrel (PNUT) - Created as a tribute to a rescued squirrel, PNUT reached the $1 mark a month after its inception and is trading at $1.27 as of late.
· Mew - A Solana meme token launched on the Raydium exchange, representing a community that aims to usher in a new age beyond dog-themed tokens.
· Snek (SNEK) - Running on the Cardano blockchain, Snek is described as a "cultural movement".
· Base Dawgz (DAWGZ) - A multi-chain meme coin operating on Ethereum, Solana, Binance Smart Chain, and Avalanche, known for its share-to-earn strategy and staking protocol.
Unblocking a transaction
The cryptocurrency world has experienced high volatility, and success is all down to timing. When your transactions on the Dogecoin network are stuck, it may be because you don't have enough DOGE to cover network fees. You can manage your DOGE balance very well, but it is difficult to estimate network fees. It is particularly frustrating in a highly liquid exchange in a volatile environment. Plasbit exchange services allow you to make a bank transfer to your walletand convert it into DOGE, so you have enough to pay network fees. It is a straightforward solution to unblock the transaction that was stuck because your DOGE balance was insufficient to cover network fees.







