If you perform a transaction on the Ethereum blockchain and your transfer is pending and stuck, there are a few things you can do to fix it. If you check on etherscan.io and you see that your ETH transaction stuck pending it could be that the transaction fee (gwei) provided for the transaction was too low, so you need to check how much gas was paid for the transaction and then you can compare it to the current market average fee on the etherscan gastracker and you may be able to use the Replace-by-Fee (RBF) method to unstuck it. You need to realize that every ethereum transaction on the ETH blockchain requires a "gas" called gwei, which is basically the fee payment to the miners who validate and secure the network. Despite the usual efficiency, you may sometimes have to leave your transfer unconfirmed and in limbo and it will be either canceled or approved by itself. This article will assist in learning about the cause of pending transactions and provide practical solutions, empowering you to take control and resolve such issues confidently.
How Do I Know If My Transaction Is Pending?
In the dynamic environment of the Ethereum network, a "pending" transaction signifies that the network has acknowledged it but not yet finalized or added to the blockchain. This state occurs after nodes verify the transaction's validity—checking for a valid signature and sufficient funds—and before miners include it in a new block. Your transaction enters a mempool, a holding area for all verified transactions awaiting miners' selection and block addition. Understanding whether your transaction is pending is essential to managing your Ethereum dealings efficiently.
Nonce Number Priority
A transaction might also be pending because it's queued behind other transactions from the same sender with lower nonces. In Ethereum, each transaction from an account has a sequential nonce, a number that represents the transaction's order. If a transaction with a lower nonce is still pending, subsequent transactions with higher nonces will remain queued until the earlier one is processed.
Monitor Gas Fees
You should monitor the gas fees during your transaction to avoid getting stuck. The gas fee is a critical determinant of transaction speed. If your offered fee is below the current average, miners might overlook your transaction in favor of more lucrative ones. PlasBit recommends that real-time gas fee information be obtained from tools like Etherscan Gas Tracker, which helps you determine an appropriate fee to prevent future delays.
How To Solve ETH Transaction Stuck Pending
When faced with a pending (stuck) Ethereum transaction, it can be a stressful experience, especially if the transaction is of a time-sensitive or significant nature. You can resolve the issue effectively by checking the transaction status and following the steps in the guides below. Remember, sometimes, the simplest solution is patience. If the network is congested, your transaction might get picked up once the congestion diminishes. It could take several hours or, in extreme cases, days.
Check Transaction Status
To check the status of your transaction, Etherscan is an invaluable tool. This blockchain explorer provides a user-friendly interface that allows you to look up your transaction using its unique hash or wallet address.
1. Visit Etherscan and Search Transaction Hash:
First, verify that your transaction is indeed stuck. Go to the Etherscan.io home page and paste your transaction hash (TxHash) in the search bar.
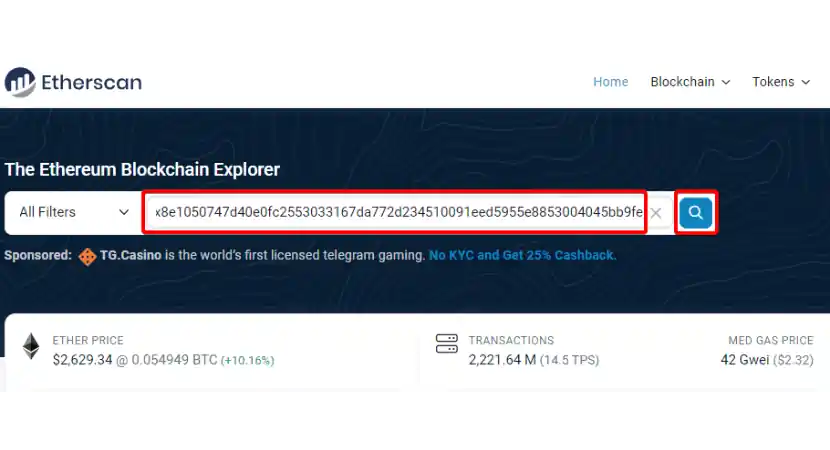
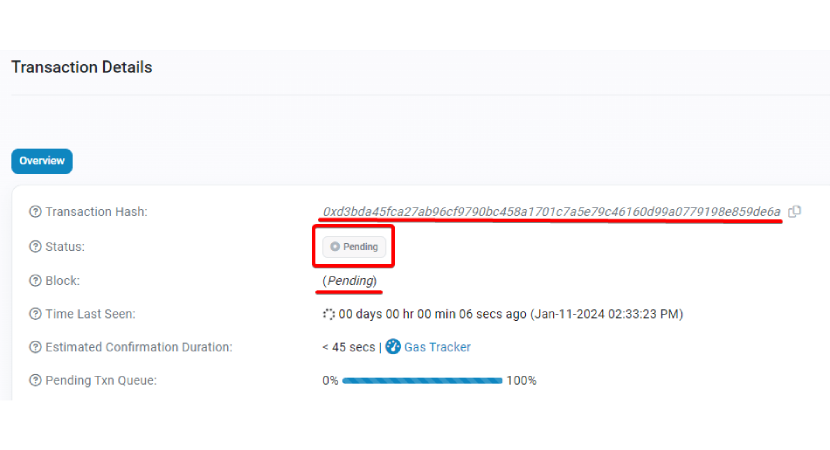
2. Check the Transaction Status:
The result will give comprehensive details about your transaction, including its current status - whether it's pending, queued, or confirmed. Several indicators can signal that your transaction is stuck in a pending state. A common sign is an extended wait time beyond typical for transaction confirmation. This outcome could be due to network congestion, where many transactions are vying for miners' attention, or it may suggest that the gas fee provided was too low, making it unattractive for miners to prioritize.
Utilize Replace-by-Fee (RBF)
When you have an ETH transaction stuck pending, you may be able to use the Replace-by-Fee (RBF) method to unstuck it. Wallets that typically support RBF include MetaMask, Ledger Live, Trezor Suite, and some other advanced wallets. Here's how you can use Etherscan and a compatible wallet to do so:
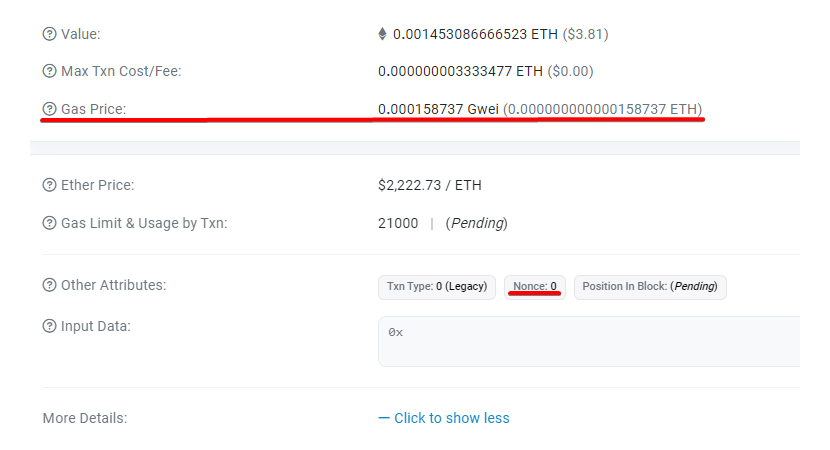
1. Check Your Transaction on Etherscan:
Follow the steps above to search for your transaction hash (TXID) and review your details. Again, check the 'Nonce' and 'Gas Price' fields.
2. Access Your Wallet's RBF Feature:
Open the wallet you utilized to send the original transaction.
3. Initiate Replace-by-Fee (RBF):
Locate the stuck transaction in your wallet's transaction history. Select 'Speed Up' or 'Replace' the transaction. This feature is usually found as a button or in the transaction details. The wallet interface should allow you to set a new gas price higher than the original transaction.
4. Set a New Gas Price:
Using the information from Etherscan, decide on a new gas price that will likely confirm your transaction. Increasing the gas price by 10-20% is recommended to incentivize miners to prioritize your new transaction.
5. Confirm and Send the New Transaction:
Once you've set the new gas price, confirm the details. Send the new transaction. Ensure the nonce is the same as the stuck transaction to replace it correctly.
6. Monitor the Transaction:
Copy the new transaction hash provided by your wallet. Go back to Etherscan and monitor the status of the new transaction. Wait for the network to confirm the new transaction. Once confirmed, the stuck transaction will be dropped.
7. Transaction Confirmation:
Once the new transaction with a higher gas fee is confirmed, your ETH will be transferred, and the issue of the stuck transaction should be resolved.
8. Verify Original Transaction Cancellation:
Check the original transaction hash on Etherscan to ensure it shows as 'Dropped' or 'Replaced .'Remember, not all wallets support the RBF feature, and not all stuck transactions can be resolved using RBF if the original transaction was sent with too low of a gas limit or if there's a network-wide congestion. Always double-check the wallet's capability to ensure it supports the RBF protocol before proceeding. If RBF is not supported, you might need to wait for the network to process the transaction or look into other methods, such as using a wallet that supports nonce management to send a new transaction with the same nonce.
Use the "Nonce" to Your Advantage
Suppose Replace-by-Fee (RBF) isn't available for your Ethereum transaction. In that case, you can still potentially unstuck your transaction by sending a 0 ETH transaction with a higher gas fee using the same nonce as the stuck transaction. Here's a step-by-step guide to using the nonce to your advantage:
1. Identify the Stuck Transaction's Nonce:
Again, visit Etherscan and search using your transaction hash in the search bar. In the transaction details, you will find its nonce - the number representing the transaction's position in the sequence of all transactions you've sent.
2. Access Your Ethereum Wallet:
Open the Ethereum wallet from which you made the stuck transaction. Ensure that the wallet allows you to set custom nonce values. Not all wallets have this feature.
3. Prepare a New ETH Transaction:
Create a new transaction. Set the recipient address to your Ethereum address and the amount to 0 ETH. Setting the nonce to the same value as the stuck transaction's nonce is also vital.
4. Set a Higher Gas Fee:
Determine an appropriate gas fee higher than the one you set for the stuck transaction. This step incentivizes miners to pick up this new transaction over the old one. You can use gas trackers or your wallet's recommended gas fees to make an educated guess.
5. Send the Transaction:
Review the transaction details to ensure the nonce and gas fees are correct. Send the 0 ETH transaction.
6. Wait for Confirmation:
Monitor the new transaction on Etherscan using the transaction hash provided by your wallet. The network should recognize the new transaction with the higher gas fee and the same nonce and process it before the stuck transaction.
7. Confirm the Stuck Transaction is Dropped:
After the new transaction is confirmed, check the status of the original stuck transaction. It should eventually be dropped or replaced in the mempool due to the nonce conflict. By using this method, you effectively "cancel" the original transaction. However, remember that this is not a guaranteed fix. The success of this method depends on the network conditions and miners' policies. Always double-check and be cautious when setting the nonce manually, as incorrect nonce usage can lead to other issues.

Why is My Ethereum Transaction Pending?
When you initiate a transaction on Ethereum, you expect it to be processed swiftly. However, sometimes, transactions don't go through as planned and remain pending longer than anticipated. Understanding why this happens is vital to preventing and resolving delayed transactions. Appropriate gas fees, network demand, and correct nonce usage are essential for a smooth transaction experience on Ethereum. By understanding these elements and how they interrelate, you're better equipped to prevent and address pending transactions, streamlining your activities on the blockchain.
Low Gas Fees
Low gas fees are among the most common reasons for a pending Ethereum transaction. Gas fees are user payments to compensate for the computational energy used to process and validate blockchain transactions. These fees are variable and fluctuate based on demand within the network - the higher the demand, the higher the fees. Miners prioritize transactions with higher gas fees since it's more profitable for them. If you set a gas fee that's too low during a time of high demand, your transaction may be outpaced by others offering more attractive fees, causing it to be stuck in a pending state. It is worth diving deeper into the concept of gas fees. Gas fees serve two primary purposes: they remunerate miners for the computational resources they expend on processing transactions and help prevent the network from being overrun by too many transactions. Users must pay for each operation within a transaction, whether it's a simple transfer of ETH or a complex smart contract interaction. Gas fees are denoted in gwei, a smaller unit of ETH, specifically, one billionth of one ETH. Calculating the total gas fee is achieved by performing a multiplication of the gas price (in gwei) by the amount of gas used. The importance of gas fees cannot be overstated. They incentivize miners to keep the network secure and operational. The Ethereum network could not confirm transactions or maintain its decentralized integrity without miners. Gas fees also help to allocate network resources fairly. By requiring users to pay for computation, the network ensures that those who value the resources most are the ones who use them.
Network Congestion
Network congestion is another factor that contributes to pending transactions. When there are a large number of users trying to make transactions at the same time, the network can become congested. This occurrence is similar to traffic during rush hour - there's only so much space, or in the case of Ethereum, computational power to process transactions promptly. During these periods of high traffic, miners can only process so many transactions, and they naturally select the ones with the highest fees. Transactions with lower fees will have to wait until the congestion decreases or until the sender decides to increase the gas fee.
Nonce Assignment
Another crucial element in the Ethereum transaction process is the nonce. A nonce is a number assigned to each transaction that indicates its order in the sequence of all transactions sent from a particular Ethereum address. It ensures that transactions are processed in the order they were sent. If you send a transaction with a nonce that's too high (skipping a number), the network will wait until all previous transactions with lower nonces are processed. This action can lead to an ETH transaction stuck pending if a previous transaction with a lower nonce is pending due to low gas fees or other issues.
Risks Associated with Increasing Gas Fees
Managing gas fees is a balancing act that requires users to stay informed about network conditions and understand the technical aspects of blockchain transactions to avoid unnecessary risks and costs. Increasing gas fees on blockchain networks can lead to risks PlasBit believes must be carefully considered to avoid unnecessary costs and transaction issues.
Overpayment:
In a volatile cryptocurrency market, gas prices can fluctuate rapidly due to network congestion or changes in demand for processing transactions. If a user sets a high gas price to ensure a transaction is processed quickly, they might end up overpaying if, shortly after, the congestion decreases and the average gas price drops. The effect is akin to buying an airline ticket at a peak price only to see the price drop substantially right after your purchase. The result is an inefficient use of resources where users pay more than necessary for the transaction to be confirmed.
Double Spending:
The nonce, a sequential number assigned to each transaction a user sends, is critical to prevent double-spending. If a user attempts to replace a transaction with a higher gas fee but fails to use the correct nonce, they could risk having both the original and new transactions confirmed by the network. It could inadvertently lead to double spending, where the exact amount is deducted twice from the user's wallet, potentially leading to financial loss and other issues related to unintended transactions.
Transaction Failure:
Increasing the gas fee for a transaction does not always guarantee its success. If the new transaction is not allocated enough gas to complete the intended operation or the smart contract execution runs into an error, the transaction may fail. In such cases, the user not only experiences a failed transaction but also loses the gas fee paid, as miners or validators are compensated for computational work even if the transaction doesn't successfully conclude. This outcome highlights the importance of setting a higher gas fee and ensuring that the transaction is well-formed and that there is enough gas to cover the entire computation.
Customizing Fees When Using the Ethereum Network
As users engage with the Ethereum network, understanding what is ETH and customizing transaction fees is paramount to ensure timely confirmations without unnecessary expense. Gas fees, the price you pay for computational efforts on the network, can be adjusted before executing a transaction. However, doing this requires a balance between paying enough to process your transaction quickly and not overspending.
Adjusting Gas Fees and Gas Limits
You're prompted to set a gas limit and a price when you initiate a transaction. The limit defines the maximum amount of gas units you're willing to spend on a transaction, while the gas price is the amount of ETH you are ready to pay per gas unit. The product of these two numbers is your maximum total fee. To adjust these settings:
1. Access Ethereum Wallet Settings:
Access your Ethereum wallet interface's "Advanced" settings before confirming the transaction.
2. Select on Gas Price and Gas Limit:
Set your preferred gas price and gas limit based on the transaction's urgency and the complexity of the contract interaction.
3. Complete Transaction:
Confirm the adjustments and execute the transaction.
Estimating the Right Fee
Strategically estimating the correct fee is vital. Setting a gas price too low may result in a stuck transaction during high network congestion. Conversely, setting it too high could mean overpaying for a transaction that might have been confirmed with a lower fee. Here are some strategies for estimating an appropriate fee:
Historical Data:
Examining the historical data of gas prices can provide insights into the average cost during similar network conditions. Platforms and tools are available that track and visualize gas price trends over time, which can help users predict future fluctuations and set a more accurate gas price for their transactions. Understanding past patterns can also guide users during network congestion, enabling them to set competitive fees that align with the prevailing market conditions.
Evaluating Pending Transactions:
By looking at the gas prices of transactions that are currently pending, users can get a real-time sense of the ongoing demand for processing power. This immediate snapshot of the network can indicate more of the required fee than historical data during rapid change. Users can adjust their fees accordingly to outbid these transactions for faster processing or choose a lower price if time is not critical.
Type and Complexity of Transaction:
The nature of the transaction itself significantly influences the necessary gas limit. A straightforward token transfer generally consumes less gas than executing complex smart contract functions. Therefore, users must tailor their gas limit to the specific needs of their transactions. It's essential to provide enough gas to cover the entire computation without wastefully allocating an excessive amount.
Network-Specific Factors:
Some blockchain networks have mechanisms to help users set appropriate fees, such as Ethereum's EIP-1559, which introduced a base fee and tips to estimate costs better. Understanding these network-specific factors can help in setting more accurate transaction fees.
Case Study: Stephen's Stuck ETH Transaction
An avid Ethereum user, Stephen encountered a frustrating obstacle when his ETH transaction stuck pending. He had attempted to transfer some ETH to another wallet for an important transaction, but it remained unconfirmed even after several hours. The Ethereum network was experiencing high congestion that day, and Stephen realized he might have set the gas fee too low. Determined to resolve the issue, Stephen turned to Etherscan, an Ethereum blockchain explorer recommended by PlasBit. Here's how he tackled the problem:
1. Transaction Details:
Stephen entered his transaction hash into Etherscan's search bar to retrieve the details of his pending transaction. He noted the gas fee he had initially set, which was below the average fee then.
2. Network Congestion:
Utilizing Etherscan's gas tracker, he observed the current gas prices and realized they were significantly higher than when he made his transaction. This situation explained why miners hadn't picked up his transaction.
3. Nonce Check:
Stephen checked the nonce number associated with his pending transaction on Etherscan, which would be crucial for his next step.
4. Sending a New Transaction:
Knowing his previous transaction was stuck due to an insufficient gas fee, Stephen sent a brand new transaction with the same nonce but a higher gas fee. He accessed his wallet, selected the advanced options, and manually set the nonce to match the stuck transaction.
5. Transaction Confirmation:
With the appropriate gas fee set, Stephen's new transaction was picked up by miners within minutes. The miners prioritized this new transaction, so the original pending transaction was dropped from the network.
6. Resolution:
Stephen's problem was solved. His ETH arrived at the intended destination, and he completed his important ETH to EUR transaction. Stephen successfully navigated his way out of a potentially stressful situation by proactively using Etherscan to assess network conditions and strategically setting a new transaction with a higher gas fee. This case study exemplifies the importance of understanding the Ethereum network's mechanics and illustrates how tools like Etherscan can empower users to resolve pending transactions efficiently.
Utilizing the Ethereum Network with Confidence
Understanding the mechanisms behind Ethereum transactions, including gas fees, nonces, and network congestion, is essential for anyone interacting with the blockchain. We've explored why transactions may become pending and approaches you can take to resolve such issues. Adjusting gas fees, properly setting the nonce, and monitoring network conditions are all crucial strategies for ensuring your transactions are processed efficiently. We delved into the tools at your disposal, such as blockchain explorers like Etherscan, which provide real-time insights into network activity and help estimate appropriate gas fees. Utilizing these resources can significantly reduce the chances of experiencing a "transaction stuck pending" scenario. Remember, you can also learn how to deal with an unconfirmed Bitcoin transaction to expand your crypto knowledge. While the Ethereum network can be complex, you can navigate it effectively with the proper knowledge and tools. Always stay informed, be prepared to adjust your strategies as network conditions change, and use the available resources to optimize your transaction experience. The blockchain landscape is ever-evolving, and keeping abreast of these changes is crucial to success in this digital frontier.







