Being involved in Bitcoin was a bit like the Wild West back in 2011. It was a world of extremes, where great opportunities came hand in hand with great risks. Back then, there weren’t nearly as many Bitcoin exchanges as we have today. The world’s biggest exchange at the time, Mt. Gox, handled over 70% of all Bitcoin transactions worldwide. At its prime, estimates suggest the exchange held around 850,000 bitcoins before the hack and Kevin Day Bitcoin managed to scoop up more than 259,684 Bitcoins for just $3,000 by taking advantage of the infamous hack that caused BTC price to plummet from $17 to $0.01 on the exchange. However, the exchange administrators canceled and reversed all trades made during the period of significant rate price drop. Apparently, Kevin managed to withdraw 643 BTC, but wasn’t able to cash them out. If Kevin kept his Bitcoin stash until early 2025, it would now be worth over $26 billion, Just let that sink in.
Who Is Kevin Day?
Kevin, originally from Nebraska, was a coder and had a background in video game development. He contributed to the tech boom of the 1990s and early 2000’s and had a successful career. Kevin helped code some of the most iconic games of that era, including Mortal Kombat, NBA Showtime, NFL Blitz, and others. These were legendary video games that made a big impact on gaming culture and many people who grew up during that time still have fond memories of them. During the early 2000s, he launched a startup during the dot com bubble. Like others at the time, his venture didn’t survive the crash. After that he started hosting websites and exploring other tech related technologies. The after effects of the dot com crash seemed to fuel his interest in internet freedom and innovation, which led to an interest in blockchain and cryptocurrency. One thing has remained constant throughout his career, and that’s diving deep into his interests, whether it’s games, tech, crypto or experimenting with other emerging ideas. He’s an early adopter and certainly seems to have an entrepreneurial spirit, as well as a lot of tech knowledge.
What Was The Kevin Day Bitcoin Controversy?
Kevin Day shot directly into the crypto community fame in 2011 for buying 259,684 BTC for just under $3,000 during a wild flash crash on Mt. Gox. The crash turned out to have been caused by a hack that manipulated the market. Once the cause of the crash was established, the Mt. Gox exchange ended up reversing the trades. This wiped out most of Kevin’s Bitcoin balance, leaving him with just a fraction of what he’d bought. The big question is, was Kevin Day simply in the right place at the right time or the wrong place at the wrong time? Here at Plasbit, we think it’s a bit of both. He was online during the crash and had funds ready to buy.
He spotted the chance to place a buy order at an insanely low price, but the crash's cause and its aftermath left him frustrated for life, haunted by what could have been if the trades hadn’t been reversed. The Kevin Day Bitcoin fortune was lost nearly as quickly as he gained it, with most of the 259,684 BTC reversed the same day. Mt. Gox had a daily withdrawal limit, and Kevin withdrew the maximum amount allowed before the rollback, which was 643 BTC. If he had held onto this stash, it would be worth millions today and make him one of the biggest holders, up there with people like KnightMB. Overall, the reaction to his conduct in crypto communities was divided. Some people defended Kevin, saying he was an innocent party who just happened to capitalize on a situation that presented itself to him. Like in this example from a Bitcointalk discussion, where a user named 'bitrebel' defended Kevin's actions, justifying his attempt to seize the opportunity and take advantage of the situation.
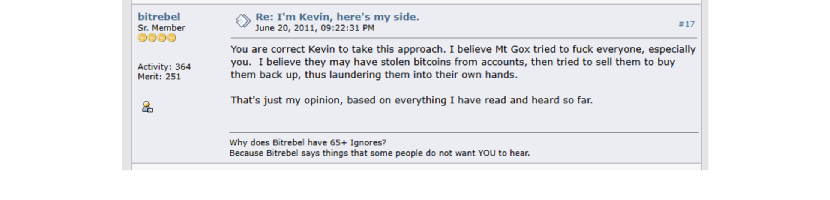
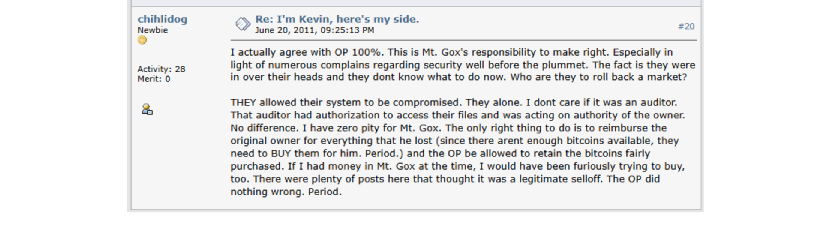
Others accused him of being an opportunist. Many say he knowingly exploited the chaos and others even accused him of knowing about the hack.
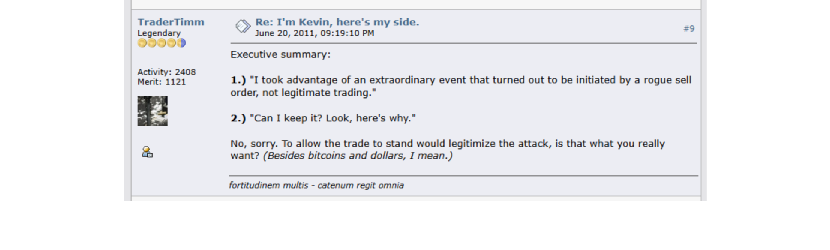
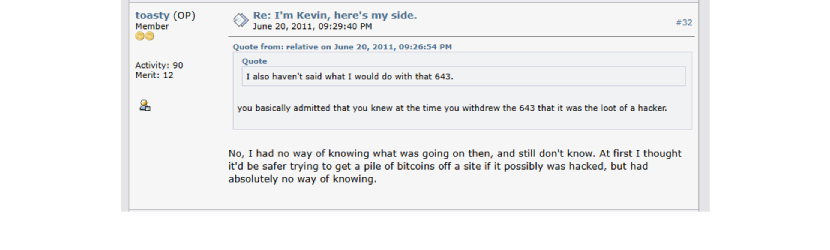
In the aftermath, the community was split between those who supported Mt. Gox’s rollback to protect the market and those who saw it as unfair.
What Caused The Bitcoin Flash Crash?
There are still questions lingering over the Mt. Gox flash crash. Was it purely caused by a hack or were there systemic issues with the exchange. Here at Plasbit, we’ve sifted through all the evidence available online and we’ve concluded that it was a combination of both the hack and some glaring vulnerabilities in Mt. Gox’s website security. The trigger for the crash happened when a hacker gained access to an account holding a huge amount of BTC and dumped it all onto the market, causing the BTC price to plummet to just $0.01. However, it was Mt. Gox’s slow trade execution and lax security measures that made the chaos much worse than it needed to be.
Kevin spotted the crash as it happened and made a quick strategic decision to place a big buy order at just above the lowest price. It was a bold move that demonstrated his sharp understanding of the price arbitrage created by the situation. After the event, the exchange admins claimed the rollback was necessary because the trades stemmed from a compromised account. However, they didn’t have clear policies for handling “erroneous trades” at the time, which fueled the controversy. Many people in the crypto community felt Mt. Gox was making up the rules as they went along. Other traders who placed low buy orders during the crash also lost their trades. Some had standing orders at $0.01 and thought they scored big, only to have their purchases wiped out. After a brief period of notoriety, Kevin pretty much disappeared from the public eye. He may still hold some Bitcoin, but the experience seems to have left him burned. Whether he’s involved in crypto today is unclear.
Behind The Scenes of The Mt. Gox BTC Flash Crash
Let’s start with some context. Mt. Gox was originally a site for trading Magic. The Gathering cards (hence the name, short for "Magic: The Gathering Online eXchange"), founded by Jed McCaleb, on July 2010. The site had been transformed into a Bitcoin exchange. In March 2011, McCaleb sold the exchange to Mark Karpelès, a French developer based out of Japan. The reason McCaleb sold the site is that it needed more attention and expertise than he could handled. By June 2011, under Karpelès’ leadership, things were already starting to look rocky.
On June 13, Mt. Gox reported the theft of 25,000 BTC (worth about $400,000 at that time) from 478 accounts. It was a bad look for an exchange that was becoming the go to place for Bitcoin trading but the drama didn’t stop there. A few days later, Mt. Gox’s user database was leaked online while a hacker, going by the alias cRazIeStinGeR, he holds the database and user credentials on Pastebin, offering it for sale and exposing vulnerabilities in the platform. On June 19, another unknown hacker made their move using the stolen credentials from a Mt. Gox auditor’s compromised computer, they accessed the exchange and started a mass sell off of Bitcoin. They dumped an enormous amount of BTC onto the market, selling at absurdly low prices, essentially creating a fake “ask” order for any willing buyers which caused Bitcoin’s price to crash from $17 to just $0.01 within minutes. It was absolute chaos as traders on the platform scrambled to place buy orders, including Kevin Day, thinking they’d just struck crypto gold but as soon as the dust settled, the price rebounded to its correct market value. Mt. Gox’s response was to freeze trading, reverse all the transactions from the flash crash timeframe, and claimed the rollback was necessary to protect the market.
This affected accounts with holdings equivalent to more than $8.75 million at the time. The exchange justified rolling back trades by saying they were fraudulent as they stemmed from a hacked account. To calm fears and prove they still had control over their reserves, Mt. Gox announced the transfer of 424,242 BTC from cold storage to one of their addresses. This was supposed to restore confidence, but for most people in the crypto community the damage was already done.
What Went Wrong for Mt. Gox?
There were three main failures in the whole Mt. Gox saga -
- Security Failures
The hacker exploited vulnerabilities in Mt. Gox’s system, including weak access controls and a lack of two factor authentication. The leaked database also showed Mt. Gox wasn’t encrypting user credentials effectively. - Slow Trade Execution
Mt. Gox’s old architecture and dated infrastructure couldn’t handle the large volume of trades. This meant the sell off spiraled out of control before anybody had time to react. - Poor Crisis Management
At Mt. Gox there didn’t seem to be a clear policy on how to handle these kinds of "erroneous trades". This employees that were left at Mt. Gox making rushed, split second decisions. As a result, the trade rollback erased legitimate trades, as well as fraudulent ones.
The controversy damaged Mt. Gox and rocked the entire crypto worldas many Bitcoin traders felt betrayed, especially those who lost money on innocent trades. Many people in the community began questioning the wisdom of storing large amounts of BTC on centralized exchanges and in a way it became the catalyst for change. There’s little doubt that Mt. Gox’s lax security was at least partly to blame for the flash crash. Some forum posts on well known sites like Bitcointalk at the time mentioned other vulnerabilities, such as leaked password hashes and poor account controls.
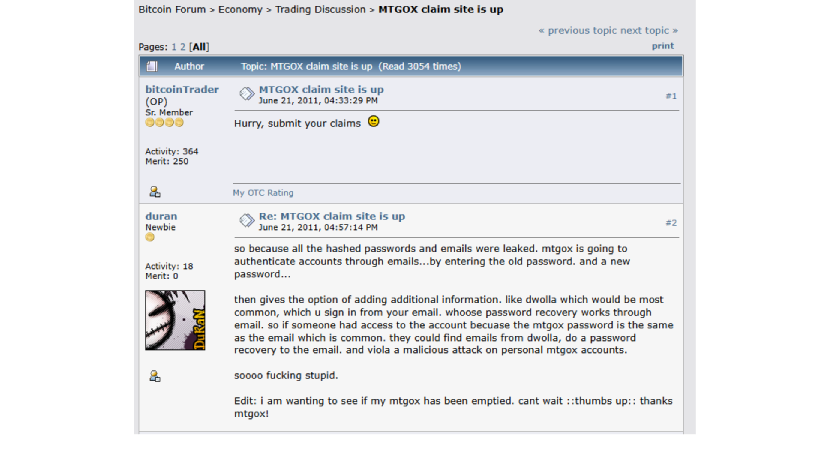
In retrospect, it looks like the exchange was a ticking time bomb just waiting to go off. It begs the question, would better security have prevented the hack and the fallout from the flash crash? This case provided a wake up call for the crypto community, especially around the risks associated with centralized exchanges as It showed how vulnerable users are when they don’t control their own assets. As a direct result of the Mt. Gox and Kevin Day Bitcoin controversy, today’s exchanges have stricter rules, stronger security, and clearer policies for handling hacks. Decentralized finance (DeFi) has become the gold standard in handling crypto trades and transactions. DeFi provides immutable transactions that aren’t subject to exchange issues or any security breaches that might occur.
The Ethics Of Crypto Trading
Kevin’s decision to withdraw 643 BTC during the flash crash chaos is still hotly debated online. Most people agree that his actions fell into a moral gray area. On one hand, you could argue he didn’t do anything illegal or break the exchange’s rules and once the trades were executed, the coins were technically his and he had the freedom to do whatever he choose including withdrawing them to an external wallet. All of his actions fell within the platform’s rules and he even followed Mt. Gox’s withdrawal limits to the letter. It’s not like Kevin deliberately pulled off a massive Bitcoin heist like James “Jimmy” Zhong who almost got away with stealing 50,676 BTC in 2021, while it was valued at more than $3.36 billion, before being arrested. But on the other hand, the market was in freefall. He must have known that something had gone terribly wrong, even if he didn’t directly know about the hack and fraudulent trades. The fact he withdrew his BTC so quickly suggests Kevin was well aware of the hack and that something is wrong. Were his actions opportunistic? Sure. Was it ethical? Well, that’s a whole different debate. The big question is, if you take advantage of a broken system, are you then complicit in its failure? From what we’ve seen, it’s unlikely Kevin was in on the hack in any way or had any involvement in the security breach.
However, there’s no denying he tried to benefit personally from the hacker’s actions. Some would say this was typical of crypto’s early days, where people were easily tempted to put profit before principles. The theft of crypto was fairly common, as were scams and exploits. Others would say that the crypto scene was based on trust and people like Kevin Day broke that trust. Maybe it’s just human nature to take advantage of “easy money” and it just highlights the need for checks and balances in our financial systems, including crypto. It makes things safer and more secure for everyone involved. Another interesting thing to look at is the psychology of the event and what drove Kevin to act while others froze. Taking advantage of the situation in high-stakes moments like this comes from a variety of factors.
● Clever Trading: It’s pretty clear that Kevin understood the mechanics of the Mt. Gox exchange and how buy orders worked. His decision to bid slightly above the $0.01 mark was a calculated approach and he wasn’t throwing money around blindly.
● Courage Under Fire: Watching Bitcoin’s price crash to $0.01 scared most traders at the time. But Kevin stayed calm and placed a buy order. Whether you call it courage, bravery, or a higher tolerance for risk than others, it takes a bold mindset to act decisively like this during a crisis.
● Pure Chance: Let’s face it, luck played a big role. Being online at the exact moment of the flash crash and having funds ready to deploy wasn’t something Kevin could plan for. Timing, in this case, was everything.
The human psychology of Kevin Day’s Bitcoin story is fascinating. Why do some people take bold risks while others sit on the sidelines? Kevin’s actions reflect a mix of instinct, knowledge, and perhaps a willingness to gamble on uncertainty.

How Crypto Exchange Security Has Evolved
Since the Mt. Gox flash crash and other crypto scandals, much has been learned from past mistakes. Security has moved on considerably and most reputable crypto exchanges are now just as secure, if not more so, than traditional banks. Many exchanges also use cold storage wallets to store users crypto. Let’s take a look at some of the security features that most exchanges now use as standard.
Two Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA is like adding a double lock to your front door, It’s a must have for most crypto exchanges these days, as people will most likely avoid those that don’t offer it. It reduces the chances of unauthorized access to almost zero and the only way a hacker can bypass it is if they have your device or phone number, as well as your login credentials. Back in the Mt. Gox days, it was alarmingly easy for hackers to get into accounts because all they needed were basic login credentials. Today, with 2FA, you need both a password and a second verification, such as biometrics or a code sent to your personal phone number or generated by an authenticator app.
Cold Wallets and Hot Wallets
In a leading exchange like Plasbit, cold and hot wallets are a no brainer as we carefully split funds between
● Hot Wallets: Online and used for day to day withdrawals and the funds are accessible but more vulnerable to attacks.
● Cold Wallets: Stored offline, making them virtually immune to hacking as these hold the bulk of user funds, meaning even if an exchange gets breached, the damage is limited only to the crypto holdings in the hot wallets. A lack of proper cold storage could lead to catastrophic losses and the crash of an entire exchange.
Encryption and Password Hashing
In the case of Mt. Gox, they didn’t even encrypt user passwords properly, which was kind of like leaving your house keys under the doormat. Modern exchanges like Plasbit use robust encryption and hash passwords with techniques like SSL, bcrypt, Secure Enclave, or Argon2. This makes it far harder for hackers to decipher stolen data, even if they manage to get their hands on it.
Multi-Signature Wallets
These are like multiple keys to unlock a vault. With multi-sig wallets, several private keys are needed to authorize a transaction. This adds a crucial layer of protection, especially for high value transfers. Even if one key is compromised, the hacker still can’t access the funds without the others.
Regulatory Accountability
As cryptocurrency has caught on and become more mainstream, governments and regulators have woken up to the risks of poorly managed exchanges. Now, most reputable platforms are obliged to meet strict standards, including the following.
● Audits: Regular security checks to identify vulnerabilities.
● Compliance Certifications: Like SOC 2, which proves an exchange meets rigorous data protection standards.
● Reporting Requirements: Exchanges have to disclose hacks, breaches, or suspicious activity quickly, making them more accountable.
This level of scrutiny was unheard of in the days of Mt. Gox and Kevin Day, but they’re now a vital part of building trust in the industry.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
DEXs emerged as a response to the vulnerabilities of centralized exchanges, like Mt. Gox. By allowing users to trade directly from their wallets, DEXs eliminate the need to trust a middleman. The benefits of DEXs is that there are no custody risks and your keys stay yours forever. But they’re not without flaws. Smart contract bugs and user errors can still cause issues. Even so, they still represent a big step toward the decentralized ethos that crypto was built on.
User Awareness
Let’s face it – security is only as strong as the user’s understanding of it. For that reason, the crypto industry has ramped up efforts to educate users on best practices, such as using hardware wallets for large holdings and always enabling 2FA. There has also been a big push on recognizing phishing scams, as this is still a big vulnerability as it allows hackers to gain access to private wallets. “Not your keys, not your coins” i.e. don’t ever give out your keys or coins to unknown source is a mantra every crypto enthusiast should live by.
Advanced Modern-Day Exchange Security Features
In recent years, increasingly sophisticated security measures have been developed to protect exchanges from such vulnerabilities.
Modern exchanges are often armed to the teeth with advanced features like the following -
● AI Driven Fraud Detection: Machine learning algorithms analyze patterns to flag suspicious activity as it happens and before it becomes a bigger problem.
● Insurance Funds: Some platforms now insure user funds, so even if a breach occurs, customers don’t lose everything.
● Emergency Trade Halts: If something like the Mt. Gox flash crash was to happen today, exchanges can freeze trading instantly to prevent further chaos.
The Future of Exchange Security
The road ahead is just as exciting, but also challenging as hackers develop more sophisticated ways to defraud people as It’s a constant game of cat and mouse. Scams and hacks will never stop happening in the crypto world, as the recent Mango Markets exploit shows. Here are some interesting new security features that are starting to emerge -
● Quantum Resistant Cryptography: Both traditional banks and crypto exchanges are starting to prepare for the day when quantum computers can break current encryption standards. Although this is still theoretical and might be quite a way off into the future, many experts believe it will happen eventually, so it’s worth paying attention to.
● More Decentralized Solutions: Increased reliance on systems where users maintain control of their assets.
● AI-Powered Monitoring: Smarter algorithms that not only detect threats but adapt to new ones in real time.
Learning from the Past, Building a Safer Future
If there’s one lesson from the Kevin Day Bitcoin saga and the Mt. Gox flash crash, it’s the importance of exchange security. Crypto's chaotic early days were characterized by ambition outpacing infrastructure, and bold opportunities being overshadowed by big risks. Today, the picture is totally different as Innovations like 2FA, cold wallets, multi-sig transactions, and the rise of decentralized exchanges have redefined security in the crypto world. It means crypto enthusiasts, traders, and investors can operate with more confidence. At Plasbit, we are dedicated to providing a secure, transparent, and user-friendly platform cause we believe all crypto holders can rest easy knowing their funds are stored in cold wallets, coupled with our personal commitment to safeguarding every amount held in our custody.